Table of Contents
8 Keywords
8.1 Data structures
The following describes keyword dependencies. Trailing ‘…’ implies that more than one node of that type can be inserted under its parent. Items enclosed in square brackets are optional. Items beginning with a capital T corresponds to keyword groups analogous to complex types in XML.
Ttop
Ttop_xdd
[r_p #] [r_wp #] [r_exp #] [gof #] [r_p_dash #] [r_wp_dash #] [r_exp_dash #]
Tglobal
[A_matrix][C_matrix][A_matrix_normalized][C_matrix_normalized]
[A_matrix_memory_allowed_in_Mbytes #]
[A_matrix_elements_tollerance #]
[A_matrix_report_on]
[fraction_of_yobs_to_resample !E]
[determine_values_from_samples]
[resample_from_current_ycalc]
[chi2_convergence_criteria !E]
[file_name_for_best_solutions $file]
[line_min] [use_extrapolation] [no_normal_equations] [use_LU]
[A_matrix_prm_filter $filter]
[out_prm_vals_per_iteration $file]... | [out_prm_vals_on_convergence $file]...
[out_prm_vals_filter $filter]
[percent_zeros_before_sparse_A #]
[quick_refine !E [quick_refine_remove !E]]
[randomise_file_out_normal $file]
[move_to_the_next_temperature_regardless_of_the_change_in_rwp]
[save_values_as_best_after_randomization]
[use_tube_dispersion_coefficients]k090
Txdd
[xdd $file [{$data}] [range #] [xye_format] [gsas_format] [fullprof_format] ]...k095
[I_parameter_names_have_hkl $start_of_parameter_name]
[hkl_m_d_th2 # # # # # # E I E]...
Tcomm_1_2_phase_1_2
Txdd_scr
[dont_merge_equivalent_reflections]
[ignore_differences_in_Friedel_pairs]
Tscr_1
[i_on_error_ratio_tolerancek105#]
[num_highest_I_values_to_keep #]
Txdd_comm_1
Error! Hyperlink reference not valid.
[crystalline_area #]
[amorphous_area #]
[d_spacing_to_energy_in_eV_for_f1_f11 !E]
[extra_X_left !E] [extra_X_right !E]
[fit_obj E [min_X !E] [max_X !E] ]...
[randomize_file_out_normal $file]
[weighting !E [recal_weighting_on_iter]]
[yobs_out $file] [ycalc_out $file] [diff_out $file]
Tcomm_1
filament_lengthk114E sample_length E receiving_slit_length E
capillary_u_cm_inv E
capillary_parallel_beam | capillary_divergent_beam
[lpsd_th2_angular_range_degrees E]...
lpsd_equitorial_divergence_degrees E
lpsd_equitorial_sample_length_mm E
[exp_conv_const E [exp_limit E] ]...
[h1 E k047h2 E k047m1 E k047m2 E]
[push_peak]…[bring_2nd_peak_to_top]…[add_pop_1st_2nd_peak]…[scale_top_peak E]…
[spv_h1 E k047spv_h2 E k047spv_l1 E k047spv_l2 E]
[stacked_hats_conv [whole_hat E [hat_height E]]...[half_hat E [hat_height Ek081…]]]...
[user_defined_convolution E min E max E]...
Tcomm_2
[lam [ymin_on_ymax #] [no_th_dependence] [Lam !E] [calculate_Lam]]
[la E k032lo E [lh E] | [lg E…]]
[prm|local E [min !E] [max !E] [del !E] [update !E] [stop_when !E] [val_on_continue !E…]]
Tphase_1
[atom_out $file [appendk134…]]
[cell_mass !E] [cell_volume !E] [weight_percent !E]
[spiked_phase_measured_weight_percentk012!E] [corrected_weight_percent !E]
[phase_out $file [append] ]...
Tphase_2
Error! Hyperlink reference not valid.
[peak_buffer_step E [report_on] ]
Tlebail
Tstr_details
[append_cartesian] [append_fractional [in_str_format] ]
[append_bond_lengths [consider_lattice_parameters] ]
[atomic_interaction N E] | [ai_anti_bump N]...k006
ai_sites_1 $sites_1 ai_sites_2 $sites_2
[ai_no_self_interation]
[ai_closest_N !E]
[ai_radius !E]
[ai_exclude_eq_0]
[ai_only_eq_0]
[box_interaction [from_N #] [to_N #] [no_self_interaction] $site_1 $site_2 N E]...
[break_if_been_there $sites !E [been_there_buffer #buffer_size] [been_there_clear_buffer !E]]
[cloud_population !E]
[cloud_save $file]
[cloud_load_xyzs $file]
[cloud_load_xyzs_omit_rwps !E]
[cloud_save_xyzs $file]
[cloud_formation_omit_rwps !E]
[cloud_extract_and_save_xyzs $file]
[cloud_number_to_extract !E]
[cloud_atomic_separation !E]
[cloud_try_accept !E]
[cloud_gauss_fwhm !E]
[grs_interaction [from_N #] [to_N #] [no_self_interaction] $site_1 $site_2 qi # qj # N E]...
[occ_merge $sites [occ_merge_radius !E…]]
[x E] [y E] [z E]
[num_posns #] [rand_xyz !E] [inter !E]
[occ $atom E beq E]…
[adps] [u11 E] [u22 E] [u33 E] [u12 E] [u13 E] [u23 E]
[sites_distance N] | [sites_angle N] | [sites_flatten N [sites_flatten_tol !E…]]
[site_to_restrain $site [ #ep [ #n1 #n2 #n3 ] ] ]...
[site_to_restrain $site [ #ep [ #n1 #n2 #n3 ] ] ]…
[swap_sites $sites_1 $sites_2]…
[fourier_map_formula !E]
[extend_calculated_sphere_to !E]
[min_grid_spacing !E]
[correct_for_atomic_scattering_factors !E]
[f_atom_type $type [f_atom_quantity !E]]…
[try_site_patterns $sites [num_patterns_at_a_time #] ]...
Thkl_lat
[a E] [b E] [c E] [al E] [be E] [ga E]
[phase_penalties $sites N [hkl_Re_Im #h #k #l #Re #Im]...]…
[accumulate_phases_and_save_to_file $file]
[accumulate_phases_when !E]
[spherical_harmonics_hkl $name]...
Trigid
[point_for_site $site [ux|ua E] [uy|ub E] [uz|uc E] ]...k121
[z_matrix $atom_1 [$atom_2 E] [$atom_3 E] [$atom_4 E] ] …
[rotate E [qx|qa E] [qy|qb E] [qz|qc E] ]...k123
[translate [tx|ta E] [ty|tb E] [tz|tc E] ]...k124
[start_values_from_site $unique_site_name]
Tout_record
[out_eqn !E]
[out_fmt $c_fmt_string]
[out_fmt_err$c_fmt_string]…
Tmin_r_max_r
Tspace_group
Miscellanous
8.2 Alphabetical listing of keywords
[a E] [b E] [c E] [al E] [be E] [ga E]
Lattice parameters in Angstroms and lattice angles in degrees.
[adps] [u11 E] [u22 E] [u33 E] [u12 E] [u13 E] [u23 E]
adps when used generates the unn atomic displacement parameters with considerations made for special positions. On termination of refinement the adps keyword is replaced with the unn parameters; see example AE1-ADPS.INP. Instead of using the adps keyword the unn parameters can be manually entered.
The unn matrix can be kept positive definite with the site dependent macro ADPs_Keep_PD; this can stabilize refinement. The ADPs_Keep_PD macro can be used after the unn parameters are created.
[amorphous_phase]
Signals that the associated phase is amorphous when calculating degree_of_crystallinity.
[A_matrix][C_matrix][A_matrix_normalized][C_matrix_normalized]
Generates the un-normalized and normalized A and correlation matrices. If do_errors is defined then C_matrix_normalized is automatically generated and appeneded to the OUT file.
[append_cartesian] [append_fractional [in_str_format] ]
Appends site fractional coordinates in Cartesian or fractional coordinates respectively to the *.OUT file at the end of a refinement. For the case of append_fractional, the in_str_format keyword formats the output in INP format.
[append_bond_lengths [consider_lattice_parameters] ]
Appends bond lengths to the end of the *.OUT file at the end of refinement. A number corresponding to equivalent positions is appended to site names.
consider_lattice_parameters includes the effects of lattice parameter errors in the calculation of bond length and bond angle errors.
An example of bond lengths output is as follows:
Y1:0 O1:0 2.23143
O2:0 2.23143 88.083
O3:0 2.28045 109.799 99.928
The first line gives the distance between the sites Y1 and O2. The first number in the second line gives the distance between sites Y1 and O2. The third number of 88.083 gives the angle between the vectors Y1 to O1 and Y1 to O2. The first number on the third line contains the distance between sites Y1 and O3. The second number in the third line contains the angle between the vectors Y1 to O3 and Y1 to O2. The third number in line three contains the angle between the vectors Y1 to O3 and Y1 to O1. Thus bond lengths correspond to the first number in each line and bond angles start from the second number. The numbers after the site name and after the ‘:’ character corresponds to the site equivalent position as found in the *.SG space group files found in the SG directory
[approximate_A]
[A_matrix_memory_allowed_in_Mbytes !E]
[A_matrix_elements_tollerance !E]
[A_matrix_report_on]
See section 5.2 for a description of approximate_A.
A_matrix_memory_allowed_in_Mbytes limits the memory used by the A matrix to a maximum of A_matrix_memory_allowed_in_Mbytes. If the matrix requires less than A_matrix_memory_allowed_in_Mbytes then the full matrix is used otherwise the matrix is treated as a sparse matrix.
A_matrix_elements_tollerance removes elements in the A matrix with values less than A_matrix_elements_tollerance. The comparison is made againts normalized elements of A such that the diagonals have a values of 1. The A matrix is made sparse when A_matrix_elements_tollerance is defined. Typical values of A_matrix_memory_allowed_in_Mbytes range from 0.0001 to 0.01.
A_matrix_memory_allowed_in_Mbytes and A_matrix_elements_tollerance can be used simultanuously.
A_matrix_report_on displays the percentage of non-zero elements in the A matrix.
[atomic_interaction N E] | [ai_anti_bump N]…
ai_sites_1 $sites_1 ai_sites_2 $sites_2
[ai_no_self_interation]
[ai_closest_N !E]
[ai_radius !E]
[ai_exclude_eq_0]
[ai_only_eq_0]
Defines an atomic interaction with the name N between sites identified by $site_1 and $site_2. For atomic_interaction E is the site interaction equation that can be a function of R and Ri. R returns the distance in Å between two atoms; these distances are updated when dependent fractional atomic coordinates are modified. The name of the atomic_interaction N can be used in equations and in particular penalty equations.
For ai_anti_bump an anti-bump interaction equations is internally generated. For anti-bumping only the ai_anti_bump is faster than using atomic_interaction. The macro AI_Anti_Bump usesai_anti_bump.
no_self_interaction prevents any interactions between equivalent positions of a site. This is useful when a general position is used to describe a special position.
ai_closest_N: interactions between $sites_1 and $sites_2 are sorted by distance and only the first ai_closest_N number of interactions are considered.
ai_radius: only the interactions between $sites_1 and $sites_2 that are within the distance ai_radius are considered.
When ai_radius and ai_closest_N are both defined then interactions from both sets of corresponding interaction are considered.
ai_exclude_eq_0: only interactions that is not the first equivalent positions in $sites_2 are considered. For example, in the following:
atomic_interaction…
ai_exclude_eq_0
ai_sites_1 Pb
ai_sites_1 “O1 O2”
the following interactions are considered:
Pb:0 and O1:n (n ¹ 0)
Pb:0 and O2:n (n ¹ 0)
where the number after the ‘:’ character corresponds to the equivalent positions of the sites.
ai_only_eq_0:only interactions between equivalent positions 0 are considered.
Functions
The atomic_interaction’ equation can be a function of the following functions:
AI_R(#ri): Returns the distance between the current site and the atom defined with Ri = #ri.
AI_R_CM: A function of no arguments that returns the geometric center of the current atom and the atoms defined in $sites_2.
AI_Flatten(#toll): A function that returns the sum of distances of the current atom and those defined in $sites_2 to an approximate plane of best fit. The plane of best fit is constructed such that the sum of the perpendicular distances to the current atom plus those defined in $sites_2 are a minimum
AI_Cos_Angle(#ri1, #ri2): Returns the Cos of the angle between the atom define as Ri=#ri1, the current atom and the atom defined as Ri=#ri2.
AI_Angle(#ri1, #ri2) : Similar to AI_Cos_Angle except that the value returned is the angle in degrees.
Examples BENZENE_AI1.INP, BENZENE_AI2.INP and BENZENE_AI3.INP demonstrates the use of the atomic_interation functions.
atomic_interaction’s can be used to apply geometric restraints. For example, an anti-bump interaction between symmetry related molecules can be formulated as follows:
atomic_interaction ai1 =
IF R < 3 THEN
(R-3)^2
ELSE
0
ENDIF
;
ai_exclude_eq_0
ai_sites_1 C*
ai_sites_1 C*
ai_radius 3
penalty = If(Cycle_Iter < 10, ai1, 0);
This example demonstrates anti-bumping between molecules for the first ten iterations of a refinement cycle.
[atom_out $file [append] ]…
Used for writing site dependent details to file. See the keyword out for a description of out_record. The Out_CIF_STR uses atom_out
[axial_conv]…
filament_length E sample_length E receiving_slit_length E
[primary_soller_angle E]
[secondary_soller_angle E]
[axial_n_beta !E]
Defines the full axial divergence model using the method of Cheary & Coelho (1998b).
filament_length, sample_length and receiving_slit_length define the length of the tube filament, sample and receiving slit in the axial plane in mm.
primary_soller_angle: primary Soller slit angle in degrees.
secondary_soller_angle: secondary Soller slit angle in degrees.
axial_n_beta: Define the number of rays emanating from a point X-ray source in the axial plane. Larger values for axial_n_beta increases both accuracy and calculation time.
The macro Full_Axial_Model simplifies the use of axial_conv.
[bkg [@] # # #…]
Defines a Chebyshev polynomial where the number of coefficients are equal to the number of numeric values appearing after the bkg keyword.
[bootstrap_errors !Ecycles]
[fraction_of_yobs_to_resample !E]
[determine_values_from_samples]
[resample_from_current_ycalc]
bootstrap_errors uses the bootstrap method of error determination (Efron & Tibshirani 1986, DiCiccio & Efron 1996, Chernick 1999). Bootstrapping comprises a series of refinements each with a fraction Yobs data modified to obtain a new bootstrap sample. The standard deviations of the refined values then become the bootstrap errors. !Ecycles corresponds to the number of refinement cycles to perform, it defaults to 200. The resulting bootstrap errors are written to the *.OUT file.
fraction_of_yobs_to_resample corresponds to the fraction of the observed data that is to be replaced each refinement cycle, it defaults to 0.37. Replacement data is by default obtained randomly from the calculated pattern obtained at the end of the first refinement cycle. If resample_from_current_ycalc is defined then replacement data are obtained from the currently completed refinement cycle. The updated Yobs data is additionally modified such that the change in Rwp is unchanged in regards to the current Ycalc.
Parameter values used at the start of each refinement cycle are obtained from the end of the first refinement cycle. val_on_continue can additionlly be used to change parameter values at the start of a cycle.
If determine_values_from_samples is defined then parameter values at the end of bootstrapping are updated with values determined from the bootstrapping refinement cycles.
Parameter values obtained at the end of each bootstrap refinement cycle is written to disk in binary format. These values are then read and processed at the end of the bootstrap process without actually storing all of the values in memory. Thus the bootstrap process has a small memory footprint.
[box_interaction [from_N #] [to_N #] [no_self_interaction] $site_1 $site_2 N E]…
Defines a site interaction with the name N between sites identified by $site_1 and $site_2. E represents the site interaction equation which can be a function of R and Ri. R returns the distance in Å between two atoms; these distances are updated when dependent fractional atomic coordinates are modified. The name of the box_interaction N can be used in equations and in particular penalty equations.
When either from_N or to_N are defined, the interactions between $site_1 and $site_2 are sorted by distance and only the interactions between the from_N and to_N are considered.
no_self_interaction prevents any interactions between equivalent positions of the same site. This is useful when a general position is used to describe a special position.
For example, the following could be used to iterate from the nearest atom to the third atom from a site called Si1:
str
site Si1…
site O1…
site O2…
site O3…
box_interaction Si1 O* to_N 2 !si1o = (R-2)^2;
penalty = !si1o;
In this example the nearest three oxygen atoms are soft constrained to a distance of 2 Angstroms by the use of the penalty function. Counting starts at zero and thus to_N is set to 2 to iterate up to the third nearest atom.
The wild card character ‘*’ used in “O*” means that sites with names starting with ‘O’ are considered. In addition to using the wild card character, the site names can be explicitly written within double quotation marks, for example:
box_interaction Si1 “O1 O2 O3” to_N 3 etc…
Interactions between Si1 and the three oxygen atoms O1, O2, O3 may not all be included, for example, if Si1 had as its nearest neighbours the following:
Si1 ↔ O1,1 at a distance of 1.0 Angstroms
Si1 ↔ O2,3 at a distance of 1.1 Angstroms
Si1 ↔ O2,1 at a distance of 1.2 Angstroms
Si1 ↔ O1,2 at a distance of 1.3 Angstroms
then two equivalent positions of site O1 and two equivalent positions of O2 are included in the interaction equation; thus no interaction between Si1-O3 is considered. To ensure that each of the three oxygens had Si1 included in an interaction equation then the following could be used:
box_interaction “O1 O2 O3” Si1 to_N 0 etc…
Thus the order of $site_1 and $site_2 is important when either from_N or to_N is defined.
The reserved parameters Ri and Break can also be used in interaction equations when either from_N or to_N is defined. Ri returns the index of the current interaction being operated on with the first interaction starting at Ri=0.
box_interaction is used for example in the Anti_Bump macro.
[break_if_been_there $sites !E [been_there_buffer #buffer_size] [been_there_clear_buffer !E]]
Breaks the current refinement cycle if the sites identified in $sites are less than !E away to a previous configuration. been_there_buffer determines the number of previous site configurations to keep. If been_there_clear_buffer is defined and it evaluates to non-zero then the “been there buffer” is cleared.
Example ALVO4-GRS.INP demonstrates the use of break_if_been_there. When the current atomic configuration is similar to a previous configuration then that particular refinement cycle is terminated and the temperature is advanced to the next temperature.
break_if_been_there is typically not used with randomize_on_errors as the latter includes its own version of remembering parameter values and breaking a cycle early.
[brindley_spherical_r_cm !E]
Used for applying the Brindley correction for spherical particles. The macro Apply_Brindley_Spherical_R_PD(R, PD) is defined as:
macro Apply_Brindley_Spherical_R_PD(R, PD)
{
brindley_spherical_r_cm = (R) (PD);
}
R is the radius of the particle in cm and PD is the packing density, a number that is not updated and not refined. Here’s an example:
xdd…
str
Apply_Brindley_Spherical_R_PD(R, PD)
MVW(0,0,0)
str
Apply_Brindley_Spherical_R_PD(R, PD)
MVW(0,0,0)
Note, that PD is incorporated by way of an equation definition for brindley_spherical_r_cm. Also, phase_MAC or MVW need not be defined as they are created as needed; their definition however is necessary in order to obtain their respective values. The Brindley correction is not applied to phases without the brindley_spherical_r_cm defined.
The Brindley correction can be applied to all phases including xo_Is. In the case of phases that do not have lattice parameters or sites then the User would need to enter values for cell_volume, cell_mass and phase_MAC in order for the Brindley correction to work and for the weight percents to be obtained. This allows for the incorporation of non-structural phases in quantitative analysis. For example, the following works as the necessary information have been included.
xo_Is
Apply_Brindley_Spherical_R_PD(.002, .6)
MVW(654, 230, 0)
phase_MAC 200
[capillary_diameter_mm E]…
capillary_u_cm_inv E
capillary_parallel_beam | capillary_divergent_beam
Calculates an aberration for capillary samples. and convolutes it into phase peaks. capillary_diameter_mm corresponds to the capillary diameter in mm and capillary_u_cm_inv the linear absorption coefficient of the sample in units of cm-1. The capillary_diameter_mm convolution corrects for peak shapes, intensities and 2Th shifts, see example CAPILLARY-SIMULATED.INP.
Use of capillary_parallel_beam results in a correction for a parallel primary beam.
Use of capillary_divergent_beam results in a correction for a divergent primary beam.
Both capillary_parallel_beam and capillary_divergent_beam assume that the capillary is fully illuminated by the beam in the equitorial plane.
[cell_mass !E] [cell_volume !E] [weight_percent !E]
[spiked_phase_measured_weight_percent !E] [corrected_weight_percent !E]
cell_mass, cell_volume and weight_percent correspond to unit cell mass, volume and weight percent of the phase within the mixture.
spiked_phase_measured_weight_percent defines the weight percent of a spiked phase. Used by the xdd dependent keyword weight_percent_amorphous to determine amorphous weight percent. Only one phase per xdd is allowed to contain the keyword spiked_phase_measured_weight_percent.
corrected_weight_percentis the weight percent after considering amorphous content as determined by weight_percent_amorphous.
The weight fraction wp for phase “p” is calculated as follows:
 | where Np = Number of phases Qp = SpMpVp/Bp Sp = Rietveld scale factor for phase p. Mp = Unit cell mass for phase p. Vp = Unit cell volume for phase p. Bp = Brindley correction for phase p. |
The Brindley correction is a function of brindley_spherical_r_cm and the phase and mixture linear absorption coefficients; the latter two are in turn functions of phase_MAC and mixture_MAC respectively, or,
Bp is function of : (LACphase-MACmixture) brindley_spherical_r_cm
where
LACphase = linear absorption coefficient of phase p, packing density of 1.
MACmixture = linear absorption coefficient of the mixture, packing density of 1.
This makes Bp a function of the weight fractions wp of all phases and thus wp as written above cannot be solved analytically. Subsequently wp is solved numerically through the use of iteration.
[chi2_convergence_criteria !E]
Convergence is determined when the change in ![]() is less than chi2_convergence_criteria for three consecutive cycles and when all defined stop_when parameter attributes evaluate to true. Example:
is less than chi2_convergence_criteria for three consecutive cycles and when all defined stop_when parameter attributes evaluate to true. Example:
chi2_convergence_criteria = If(Cycle_Iter < 10, .001, .01);
[circles_conv E]…
Defines em in the convolution function:
(1 - ½em / e½½) for e = 0 to em
that is convoluted into phase peaks. em can be greater than or less than zero. circles_conv is used for example by the Simple_Axial_Model macro.
[cloud $sites]…
[cloud_population !E]
[cloud_save $file]
[cloud_save_xyzs $file]
[cloud_load_xyzs $file]
[cloud_load_xyzs_omit_rwps !E]
[cloud_formation_omit_rwps !E]
[cloud_try_accept !E]
[cloud_gauss_fwhm !E]
[cloud_extract_and_save_xyzs $file]
[cloud_number_to_extract !E]
[cloud_atomic_separation !E]
cloud allows for the tracking of atoms defined in $sites in three dimensions. It can be useful for determining the average positions of heavy atoms or rigid bodies during refinement cycles. For example, a dummy atom, “site X1” say, can be placed at the center of a benzene ring and then tracked as follows:
continue_after_convergence
…
cloud “X1”
cloud_population 100
cloud_save SOME_FILE.CLD
On termination of refinement the CLD file is saved; it can be viewed using the rigid body editor of the GUI; see examples AE14-12.INP for a cloud example. cloud_population is the maximum number of population members. Each population member comprises the fractional coordinates of $sites and an associated Rwp value.
cloud_save_xyzs saves a cloud populations to file.
cloud_load_xyzs loads and reuses previously saved populations. cloud_load_xyzs_omit_rwps can be used to exclude population membes whilst loading; it can be a function of Get(Cloud_Rwp) where Cloud_Rwp is the associated Rwp of a population member.
cloud_formation_omit_rwps can be used to limit population membes in the formation of CLD files; it can be a function of Get(Cloud_Rwp).
cloud_try_accept accepts population members if it evaluates to non-zero and if the best Rwp since the last acceptance is less than a present population member or if the number of members is less than cloud_population. If the number of population members equals cloud_population then the population member with the lowest Rwp is discarded. cloud_try_accept is evaluated at the end of each refinement cycle; it default value is true. Here’s are some examples:
cloud_try_accept = And(Cycle, Mod(Cycle, 50);
cloud_try_accept = T == 10;
cloud_gauss_fwhm is the full width at half maximum of a three dimensional Gaussian that is used to fill the cloud.
cloud_extract_and_save_xyzs searches the three dimensional cloud for high densities and extracts xyz positions; these are then saved to $file. cloud_number_to_extract defines the number of positions to extract and cloud_atomic_separation limits the atomic separation during the extraction. The actual number of positions extracted may be less than cloud_number_to_extract depending on the cloud.
[conserve_memory]
Deletes temporary arrays used in intermediate calculations; memory savings of up to 70% can be expected on some problems with subsequent lengthening of execution times by up to 40%. When approximate_A is used on dense matrices then conserve_memory can reduce memory usage by up to 90%.
[continue_after_convergence]
Refinement is continued after convergence. Before continuing the following actions are performed:
val_on_continue equations for independent parameters are evaluated
randomize_on_errors process is performed
rand_xyz processes are performed
Also, when val_on_continue is defined then the corresponding parameter is not randomized according to randomize_on_errors.
[convolution_step #]
An integer defining the number of calculated data points per measured data point. It may be useful to increase this number when the measurement step is large. convolution_step is set to 1 by default. Only when the measurement step is greater than about 0.03 degrees 2Th or when high precision is required is it necessary to increase convolution_step.
[default_I_attributes E]
Changes the attributes of the I parameter, for example,
xo_Is
default_I_attributes 0 min 0.001 val_on_continue 1
Useful when randomising lattice parameters during Le Bail refinements with continue_after_convergence.
[degree_of_crystallinity #]
[crystalline_area #]
[amorphous_area #]
degree_of_crystallinity reports on the degree of crystallinity which is calculated as follows:
degree_of_crystallinity = 100
Get(crystalline_area)/(Get(crystalline_area)+Get(amorphous_area));
crystalline_area and amorphous_area corresponds to the sum of the numerical areas under the crystallines phases and amorphous phases respectively. Phases that have amorphous_phase defined are treated as amorphous phases in the calculation.
[d_Is]…
[d E I E]…
Defines a phase type that uses d-spacing values for generating peak positions. d corresponds to the peak position in d-space in Å and I is the intensity parameter before applying any scale_pks equations.
[do_errors]
Errors for refined parameters (ESD's) and a correlation matrix are calculated at the end of refinement. The correlation matrix if defined using C_matrix_normalized is updated, if not defined then C_matrix_normalized is automatically defined and appeneded to the OUT file.
[d_spacing_to_energy_in_eV_for_f1_f11 !E]
Can be a function of the reserved parameter D_spacing. Changes f' and f“ (see section 7.1) to correspond to energies as given by d_spacing_to_energy_in_eV_for_f1_f11. Used for refining on energy dispersive data, for example,
' E(eV) = 10^5 / (8.065541 Lambda(A))
prm !detector_angle_in_radians = 7.77 Deg_on_2;
prm wavelength = 2 D_spacing Sin(detector_angle_in_radians);
prm energy_in_eV = 10^5 / (8.065541 wavelength);
pk_xo = 10^-3 energy_in_eV + zero;
d_spacing_to_energy_in_eV_for_f1_f11 = energy_in_eV;
See example ED_SI_STR.INP.
[exclude #ex1 #ex2]…
Excludes an x-axis region between #ex1 and #ex2. The macro “Exclude” simplifies the use of exclude. Example CEO2.INP demonstrates the use of excluded regions.
[exp_conv_const E [exp_limit E] ]…
Defines em in the convolution function:
Exp(Ln(0.001) e / em ) for e = 0 to exp_limit
that is convoluted into phase peaks. exp_conv_const is used by the Absorption and Absorption_With_Sample_Thickness_mm macros. If exp_limit is not defined then it defaults to em. em can be greater than or less than zero.
[extra_X_left !E] [extra_X_right !E]
Determines the extra range to which hkls are generated. For TOF data extra_X_left is typically used. For x-ray data then extra_X_right is typically used. Both default to 0.5.
[file_name_for_best_solutions $file]
Appends INP file details to $file during refinement with independent parameter values updated. The operation is performed every time a particular convergence gives the best Rwp. For example, suppose that at convergence the following was obtained:
Rwp:
30 All prms appended to file in INP format
20 All prms appended to file in INP format
35
40
15 All prms appended to file in INP format
18
10 All prms appended to file in INP format
15
[fit_obj E [min_X !E] [max_X !E] ]…
fit_obj's allows the insertion of User defined functions, see example PVS.INP. fit_obj’s can be a function of X.
min_X and max_X define the x-axis range of the fit_obj; if min_X is omitted then the fit_obj is calculated from the start of the x-axis; similarly if max_X is omitted then the fit_obj is calculated to the end of the x-axis.
[fourier_map !E]
[fourier_map_formula !E]
[extend_calculated_sphere_to !E]
[correct_for_atomic_scattering_factors !E]
[f_atom_type $type f_atom_quantity !E]…
If fourier_map is non-zero then a Fourier map is calculated on refinement termination and shown in the OpenGL window; maps can be calculated for x-ray or neutron single crystal or powder data, see test examples FOURIER-MAP-AE14.INP and FOURIER-MAP-CIME.INP. The type of map is determined by fourier_map_formula which can be a function of the reserved parameter names Fcalc, Fobs and D_spacing; here are some examples:
fourier_map_formula = Fobs; ‘ The default
fourier_map_formula = 2 Fobs - Fcalc;
Fobs corresponds to the obserbed structure moduli; in the powder data case Fobs is calculated from the Rietveld decomposition formula. Phases are determined from Fcalc.
Reflections that are missing from within the Ewald sphere are included with Fobs set to Fcalc. If extend_calculated_sphere_to is defined then the Ewald sphere is extended.
scale_pks definitions are removed from Fobs. In the event that scale_pks evaluates to zero for a particular reflection then Fobs is set to Fcalc; the number of Fobs reflections set to Fcalc is reported on.
[gauss_fwhm E]…
Defines the FWHM of a Gaussian function to be convoluted into phase peaks. gauss_fwhm is used for example by the CS_G and Strain_G macros.
[hkl_plane $hkl] …
Used by the OpenGL viewer to display hkl planes, see the CeO2.STR file in the “Rigid” directory. Here are some examples:
str…
hkl_plane 1 1 1
hkl_plane “2 -2 0”
[grs_interaction [from_N #] [to_N #] [no_self_interaction] $site_1 $site_2 qi # qj # N E]…
Defines a GRS interaction with a name of N between sites identified by $site_1 and $site_2. E represents the GRS interaction equation that can be a function of R, which returns the distance in Angstroms between two atoms; these distances are updated when dependent fractional atomic coordinates are modified. The name of the grs_interaction N can be used in equations and in particular penalty equations.
When either from_N or to_N are defined, the interactions between $site_1 and $site_2 are sorted by distance and only the interactions between the from_N and to_N are considered.
no_self_interaction prevents any interactions between equivalent positions of the same site. This is useful when a general position is used to describe a special position.
qi and qj corresponds to the valence charges used to calculate the Coulomb sum for the sites $site_1 and $site_2 respectively.
grs_interaction is typically used for applying electrostatic restraints in inorganic materials. The GRS_Interaction macro simplifies the use of grs_interaction.
[hat E [num_hats #] ]…
Defines the X-axis size of an impulse function that is convoluted into phase peaks. num_hats corresponds to the number of hats to be convoluted. num_hats is set to 1 by default. hat is used for example by the Slit_Width and Specimen_Tilt macros.
[hkl_Is]…
[lp_search !E]
[I_parameter_names_have_hkl $start_of_parameter_name]
[hkl_m_d_th2 # # # # # # I E]…
Defines a phase type that uses hkls for generating peak positions.
lp_search uses a new indexing algorithm that is independent of d-spacing extraction; lp-search-pbso4.inp demonstrates its use. lp_search minimizes on a new figure of merit function that gives a measure of correctness for a particular set of lattice parameters. More specifically the figure of merit function assigns parts of the diffraction pattern to peaks and then sums the absolute values of the products of the diffraction intensities multiplied by the distance to the peaks:
![]() where the summation in ‘j’ is over the calculated Bragg positions 2q0 and the summation in ‘i’ is over part of the diffraction pattern such that (2q0, j-1 + 2q 0, j.)/2 < 2qi < (2q 0, j+1 + 2q0, j.)/2. The method avoids difficulties associated with extracting d-spacings from complex patterns comprising heavily overlapped lines; the primary difficulty being that of ascertaining the number of lines present.
where the summation in ‘j’ is over the calculated Bragg positions 2q0 and the summation in ‘i’ is over part of the diffraction pattern such that (2q0, j-1 + 2q 0, j.)/2 < 2qi < (2q 0, j+1 + 2q0, j.)/2. The method avoids difficulties associated with extracting d-spacings from complex patterns comprising heavily overlapped lines; the primary difficulty being that of ascertaining the number of lines present.
I_parameter_names_have_hkl gives generated Intensity parameters a name starting with $start_of_parameter_name and ending with the corresponding hkl.
hkl_m_d_th2: The numbers after the keyword hkl_m_d_th2 define h k l m d and 2q values, where
h, k, l : Miller indices
m : multiplicity.
d and th2 : d and 2q values (not used by).
I : Peak intensity parameter before applying any scale_pks.
If no hkl_m_d_th2 keywords are defined then the hkls are generated using the space group; the generated hkl_m_d_th2 details are appended at the end of the space_group keyword on refinement termination. Intensity parameters are given an initial starting value of 1. If the Le Bail keyword is not defined then the intensity parameters are given the unique code of @ .
For example, the following input segment:
xdd quartz.xdd
…
hkl_Is
Hexagonal(4.91459, 5.40603)
space_group P_31_2_1
will generate the following OUT file:
xdd quartz.xdd
…
hkl_Is
Hexagonal(4.91459, 5.40603)
space_group P_31_2_1
load hkl_m_d_th2 I
{
1 0 0 6 4.25635 20.85324 @ 3147.83321
1 0 1 6 3.34470 26.62997 @ 8559.23955
1 0 -1 6 3.34470 26.62997 @ 8559.23955
…
}
The Create_hklm_d_Th2_Ip_file macro creates an hkl file listing from structures in the same format as the “load hkl_m_d_th2 I” as shown above. Even though the structure would have no sites, the weight_percent keyword can still be used; it will use whatever value is defined by cell_mass in order to calculate weight_percent.
[hkl_Is_from_hkl4]
[i_on_error_ratio_tolerance #]
[num_highest_I_values_to_keep #num]
hkl_Is_from_hkl4 is used for generating a powder pattern from single crystal data in ShelX HKL4 format, see example HKL4_TO_PP.INP.
[iters #]
The maximum number of refinement iterations, iters is set to 500000 by default
[lam [ymin_on_ymax #] [no_th_dependence] [Lam !E] [calculate_Lam]]
[la E lo E [lh E] | [lg E]]…
Defines an emission profile where each ”[la E lo E [lh E] | [lg E] ]“ determines an emission profile line, where
la: Area under the emission profile line
lo: Wavelength in [Å] of the emission profile line
lh: HW in mÅ of a Lorentzian convoluted into the emission profile line.
lg: HW in mÅ of a Gaussian convoluted into the emission profile line.
ymin_on_ymax determines the x-axis extent to which an emission profile line is calculated. It is set to 0.001 by default.
no_th_dependence defines an emission profile that is 2q independent. Allows the use of non-X-ray data or fitting to negative 2q values.
Lam defines the value to be used for the reserved parameter Lam. When Lam is not defined then the reserved parameter Lam is defined as the wavelength of the emission profile line with the largest la values. Note that Lam is used to determine the Bragg angle.
calculate_Lam calculates Lam such that it corresponds to the wavelength at the peak of the emission profile. Lam needs to be set to an approximate value corresponding to the peak of the emission profile.
See section 6 for a description of emission profiles.
[lebail #]
A 1 for the lebail keyword flags the use of the Le Bail method for peak intensity extraction.
[line_min] [use_extrapolation] [no_normal_equations] [use_LU]
no_normal_equations prevents the use of normal equations in the minimization routine; it is useful when the effects of line minimization only is sought or when there are a large number of parameters being refined. Refer to section 5 for a description of the minimization routines .
[lor_fwhm E]…
Defines the FWHM of a Lorentzian function that is convoluted into phase peaks. lor_fwhm is used for example by the CS_L and Strain_L macros.
[lpsd_th2_angular_range_degrees E]…
lpsd_equitorial_divergence_degrees E
lpsd_equitorial_sample_length_mm E
Calculates an aberration for a Linear Position Sensitive Detector and convolutes it into phase peaks. lpsd_th2_angular_range_degrees corresponds to the angular range of the LPSD in 2Th degrees. lpsd_equitorial_divergence_degrees the equitorial divergence in degrees of the primary beam andlpsd_equitorial_sample_length_mm is the lengths of the sample in the equitorial plane.
The lpsd_th2_angular_range_degrees convolution corrests for peak shapes, intensities and 2Th shifts; see example LPSD-SIMULATED.INP.
[marquardt_constant !E]…
Allows for changing the Marquardt constants, the Simulated_Annealing_1 macro changes the Marquardt constants as follows:
load marquardt_constant { 0 1 }
[min_r #] [max_r #]
Defines the minimum and maximum radii for calculating bond lengths. min_r and max_r are by default set to 0 and 3.2 Å respectively.
[mixture_density_g_on_cm3 !E]
Calculates the density of the mixture assuming a packing density of 1, see also mixture_MAC.
[mixture_MAC !E]
Calculates the mass absorption coefficient in cm2/g for a mixture as follows:
![]() where wi and (m/r)i is the weight percent and phase_MAC of phase i respectively. Errors are reported for phase_MAC and mixture_MAC.
where wi and (m/r)i is the weight percent and phase_MAC of phase i respectively. Errors are reported for phase_MAC and mixture_MAC.
The following example provides phase and mixture mass absorption coefficients.
xdd…
mixture_MAC 0
str…
phase_MAC 0
The macros Mixture_LAC_1_on_cm, Phase_LAC_1_on_cm and Phase_Density_g_on_cm3 calculates the mixture and phase linear absorption coefficients (for a packing density of 1) and phase density, for example:
xdd…
Mixture_LAC_1_on_cm(0)
str…
Phase_Density_g_on_cm3(0)
Phase_LAC_1_on_cm(0)
Errors for these quantities are also calculated. Mass absorption coefficients obtained from NIST at http://physics.nist.gov/PhysRefData/XrayMassCoef are used to calculate mixture_MAC and phase_MAC.
[neutron_data]
Signals the use of neutron atomic scattering lengths.Scattering lengths for isotopes can be used by placing the isotope name after “occ” as in:
occ 6Li 1
occ 36Ar 1
The scattering lengths data, contained in the file NEUTSCAT.CPP, is from
www.ccp14.ac.uk/ccp/web-mirrors/neutrons/n-scatter/n-lengths/LIST~1.HTM
Constant wavelength neutron diffraction requires a Lorentz correction using the Lorentz_Factor macro (defined in TOPAS.INC); it is defined as follows:
scale_pks = 1 / (Sin(Th)^2 Cos(Th));
[no_LIMIT_warnings]
Surpresses LIMIT_MIN and LIMIT_MAX warning messages.
[normalize_FCs]
If defined then site fractional coordinates are normalized. Normalization of a particular fractional coordinate does not occur if it has min/max limits, is part of a rigid body or part of a site constraint of any kind.
[numerical_area E]
Returns the numerically calculated area under the phase.
[occ_merge $sites [occ_merge_radius !E]]…
occ_merge rewrites the site occupancy of the sites defined in $sites in terms of their fractional atomic coordinates (Favre-Nicolin and R. Cerny 2002). This is useful during structure solution for merging ocathedra or other types of defined rigid bodies. It is also useful for identifying special positions as seen in the example PBSO4-DECOMPOSE.INP.
In the present implementation $sites are thought of as spheres with a radius occ_merge_radius. When two atoms approach within a distance less than the sum of their respective occ_merge_radius’s then the spheres intersect. The occupancies of the sites, occ_xyz, thus become:
occ_xyz = 1 / (1 + Intersection fractional volumes)
In this way any number of sites can be merged.
Sites appearing in $sites cannot have their occupancies refined. On termination of refinement the occ parameter values are updated with their corresponding occ_xyz.
[omit_hkls !E]
Allows for the filtering of hkls using the reserved parameter names of H, K, L and D_spacing. More than one omit_hkls can be defined, for example:
omit_hkls = If(And(H==0, K==0), 1, 0);
omit_hkls = And(H==0, K==1);
omit_hkls = D_spacing < 1;
[one_on_x_conv E]…
Defines em in the convolution function:
(4 ½em e½) -½ for e = 0 to em
that is convoluted into phase peaks. emcan be greater than or less than zero. one_on_x_conv is used for example by the Divergence macro.
[only_penalties]
Instructs the minimization procedure to minimize on penalty functions only. The only_penalties switch is assumed when there are only penalties to minimize, i.e. when there are no observed data. Note, parameters that are not functions of penalties are not refined.
[out_A_matrix $file]
[A_matrix_prm_filter $filter]
out_A_matrix outputs the least squares A matrix to the file $file; used in the Out_for_cf macro. Output can be limited by using A_matrix_prm_filter, here’s an example for outputting A matrix elements corresponding to parameters with names starting with ‘q’:
out_A_matrix file.a
A_matrix_prm_filter q*
[out $file [append] ]…
[out_record]
[out_eqn !E]
[out_fmt $c_fmt_string]
[out_fmt_err $c_fmt_string]…
Used for writing parameter details to a file. The details are appended to $file when append is defined. out_eqn defines the equation or parameter to be written to $file using the out_fmt. $c_fmt_string describes a format string in c syntax containing a single format specified for a double precision number. out_fmt_err defines the $c_fmt_string used for formatting the error of eqn.
Both out_fmt and out_fmt_err requires an out_eqn definition. out_fmt can be used without out_eqn for writing strings. The order of out_fmt and out_fmt_err determines which is written to file first; thus if out_fmt_err is defined first then it will be operated on first.
The following example illustrates the use of out using the Out macros.
xdd…
out “sample output.txt” append
str…
CS_L(cs_l, 1000)
Out_String(“\tCrystallite Size Results:\n”)
Out_String(“\t=========================\n”)
Out(cs_l, “\tCrystallite Size (nm):\t%11.5f”,
“\tError in Crystallite Size:\t%11.5f\n”)
out provides a means of defining individual refinement result files, see example OUT-1.INP.
[out_rwp $file]
Outputs a list of Rwp values encountered during refinement to the file $file.
[out_prm_vals_per_iteration $file]… | [out_prm_vals_on_convergence $file]…
[out_prm_vals_filter $filter]
Outputs refined parameter values per iteration or on convergence into the file $file. In the absence of out_prm_vals_filter then all parameters are outputted otherwise only parameters with names defined in out_prm_vals_filter are considered where $fliter can contain the wild card charatcter ’*’ and the negation character ’!’, for example:
out_prm_vals_per_iteration PRM_VALES.TXT
out_prm_vals_filter “* !u*”
More than one out_prm_vals_per_iteration/out_prm_vals_on_convergence can be defined outputting different parameters into different files depending on the corresponding out_prm_vals_filter.
[peak_type $type]
Sets the peak type for a phase. The following peak_type’s are available:
| Peak type | $type | Parameters |
| Fundamental Parameters | fp | |
| Pseudo-Voigt | pv | [pv_lor E pv_fwhm E] pv_lor is the Lorentzian fraction of the peak profile(s). pv_fwhm is the FWHM of the peak profile(s). |
| Split-PearsonVII | spvii | [h1 E h2 E m1 E m2 E] The sum of h1 and h2 gives the FWHM of the composite peak. m1, m2 are the PearsonVII exponents of the left and right composite peak, respectively. |
| Split-PseudoVoigt | spv | [spv_h1 E spv_h2 E spv_l1 E spv_l2 E] The sum of spv_h1 and spv_h2 gives the full width at half maximum of the composite peak. spv_l1, spv_l2: the Lorentzian fractions of the left and right composite peak, respectively. |
[peak_buffer_step E [report_on]]
As the shapes of phase peaks do not change significantly over a short 2q range, a new peak shape is calculated only if the position of the last peak shape calculated is more than the distance defined by peak_buffer_step. Various stretching and interpolation procedures are used in order to calculate in-between peaks. See also section 6.4.
The reserved parameter names of H, K, L, M or parameter names associated with the keywords sh_Cij_prm and hkl_angle when used in the peak convolution equations result in irregular peak shapes over short 2q ranges and thus a separate peak shape is calculated for each peak.
When defined report_on causes the display of the number of peaks in the peaks buffer.
peak_buffer_step is set to 500*Peak_Calculation_Step by default.
[penalty !E]…
Defines a penalty function that can be a function of other parameters. Penalties are useful for stabilizing refinements as in for example their use in bond-length restraints.
Example HOCK.INP uses penalties to minimize on the Hock and Schittkowski problem number 65 function.
prm x1 1 min -4.5 max 4.5 val_on_continue = Rand(-4.5, 4.5); del .01
prm x2 1 min -4.5 max 4.5 val_on_continue = Rand(-4.5, 4.5); del .01
prm x3 1 min -5.0 max 5.0 val_on_continue = Rand(-5.0, 5.0); del .01
' Hock and Schittkowski problem number 65 function
penalty = (x1-x2)^2 + (1/9) (x1 + x2 - 10)^2 + (x3 - 5)^2; : 0
prm contraint_1 = x1^2 + x2^2 + x3^2;
penalty = If(contraint_1 < 48, 0, (contraint_1-48)^2); : 0
The next example applies a User defined penalty function to lattice and crystallite size parameters, which are expected to be 5.41011 Å and 200 nm respectively:
str…
Cubic(lp_ceo2 5.41011)
penalty = (lp_ceo2-5.41011)^2;
CS_L(cs_l, 200)
penalty =(cs_l-200)^2;
Minimizing on penalty functions in the presence of observed data is possible with the use of the only_penalties keyword.
[penalties_weighting_K1 !E]
Defines the weighting K1 given to penalty functions as defined in Eq. (5‑2). penalties_weighting_K1 is set to 1 by default.
[percent_zeros_before_sparse_A #]
Defines the percentage of the A matrix than can be zero before sparse matrix methods are invoked. The default value is 60%.
[phase_MAC !E]
Calculates the mass absorption coefficient in cm2/g for the current phase. See description for mixture_MAC.
[phase_out $file [append] ]…
Used for writing phase dependent details to file. See the keyword out for a description of out_record. The Create_hklm_d_Th2_Ip_file uses phase_out.
[pk_xo E]
Provides a mechanism for transforming peak position to an x-axis position. For example, the peak position for neutron time-of-flight data is typically calculated in time-of-flight space, tof, or:
tof = t0 + t1 dhkl + t2 dhkl2
where t0 and t1 and t2 are diffractometer constants. pk_xo can be used to refine TOF data as shown in examples TOF_Balzar_sh1.inp and TOF_Balzar_br1.inp.
[phase_name $phase_name]
The name given to a phase; used for reporting purposes.
[phase_penalties $sites N]…[hkl_Re_Im #h #k #l #Re #Im]…
[accumulate_phases_and_save_to_file $file]
[accumulate_phases_when !E]
phase_penalties for a single hkl is defined as follows:
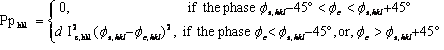 where
where ![]() = assigned phase,
= assigned phase, ![]() = calculated phase, Ic = calculated intensity and d is the reflection d-spacing. The name N returns the sum of the phase_penalties and it can be used in equations and in particular penalty equations.
= calculated phase, Ic = calculated intensity and d is the reflection d-spacing. The name N returns the sum of the phase_penalties and it can be used in equations and in particular penalty equations. ![]() is calculated from sites identified in $sites.
is calculated from sites identified in $sites.
#h, #k, #l are user defined hkls; they are used for formulating the phase penalties. #Re and #Im are the real and imaginary parts of ![]() . An example use of phase penalties (see examples AE14-12.INP and AE5-AUTO.inp) is as follows:
. An example use of phase penalties (see examples AE14-12.INP and AE5-AUTO.inp) is as follows:
penalty = pp1;
phase_penalties * pp1
load hkl_Re_Im
{
0 1 2 1 0
1 0 -2 1 0
1 -2 -1 1 0
}
hkls chosen for phase penalties should comprise those that are of high intensity, large d-spacing and isolated from other peaks to avoid peak overlap. Origin defining hkls are typically chosen.
accumulate_phases_and_save_to_file saves the average phases collected to $file. Phases are collected when accumulate_phases_when evaluates to true; accumulate_phases_when defaults to true. Here’s an example use:
temperature 1
temperature 1
temperature 1
temperature 1
temperature 10
…move_to_the_next_temperature_regardless_of_the_change_in_rwp
accumulate_phases_and_save_to_file SOME_FILE.TXT
accumulate_phases_when = T == 10;
Here phases with the best Rwp since the last accumulation are accumulated when the current temperature is 10.
[process_times]
Displays process times on termination of refinement.
[quick_refine !E [quick_refine_remove !E]]
quick_refine removes parameters that influence ![]() in a small manner during a refinement cycle. Use of quick_refine speeds up simulated annealing, see for example the macro Auto_T which is used in example AE1-AUTO.INP. All refined parameters are reinstated for refinement at the start of subsequent cycles. Large quick_refine values aggressively removes parameters and convergence to low
in a small manner during a refinement cycle. Use of quick_refine speeds up simulated annealing, see for example the macro Auto_T which is used in example AE1-AUTO.INP. All refined parameters are reinstated for refinement at the start of subsequent cycles. Large quick_refine values aggressively removes parameters and convergence to low ![]() maybe hindered. A value of 0.1 works well.
maybe hindered. A value of 0.1 works well.
quick_refine has the following consequences:
- The degree of parameter randomization increases with increasing values of quick_refine. Thus randomization should be reduced as quick_refine increases. Alternatively randomize_on_errros can be used which automatically determines the amount a parameter is randomized.
quick_refine_removeremoves a parameter from refinement if it evaluates to non-zero or reinstates a parameter if it evaluates to zero. It can be a function of the reserved parameters QR_Removed or QR_Num_Times_Consecutively_Small and additionally global reserved parameter names such as Cycle_Iter, Cycle and T. If quick_refine_remove is not defined then the removal scheme of section 5.6 is used and parameters are not reinstated until the next refinement cycle.
In most refinements the following will produce close to the lowest ![]() and in a shorter time period (see for example PAWLEY1.INP).
and in a shorter time period (see for example PAWLEY1.INP).
quick_refine .1
quick_refine_remove =
IF QR_Removed THEN
0 ' reinstate the parameter
ELSE
IF QR_Num_Times_Consecutively_Small > 2 THEN
1 ' remove the parameter
ELSE
0 ' dont remove the parameter
ENDIF
ENDIF;
[randomize_file_out_normal $file]
Randomizes the calculated pattern Yc using a Normal distribution and writes Yc to the file $file.
[rand_xyz !E]
If continue_after_convergence is defined then rand_xyz is executed at the end of a refinement cycle. It adds to the site fractional coordinate a vector u,the direction of which is random and the magnitude in Å is:
|u| = T rand_xyz
where T is the current temperature. Thus to add a shift to an atom between 0 and 1 Å the following could be used:
temperature 1
site . . . occ 1 C beq 1 rand_xyz = Rand(0,1);
Note that only fractional coordinates (x, y, z) that are independent parameters are randomized.
[r_bragg #]
Reports on the R-Bragg value. R-Bragg is independent of hkl's and thus can be calculated for all phase types that contain phase peaks.
[rebin_with_dx_of !E]
rebin_with_dx_of rebins the observed data, see example CLAY.INP. It can be a function of the reserved parameter X as demonstrated in tof_bank2_1.inp. If rebin_with_dx_of evaluates to a constant then the observed data is re-binned to equal x-axis steps. For observed data that is of unequal x-axis steps then re-binning provides a means of converting to equal x-axis steps.
[rigid]…
[point_for_site $site [ux|ua E] [uy|ub E] [uz|uc E] ]…
[in_cartesian] [in_FC]
[z_matrix $atom_1 [$atom_2 E] [$atom_3 E] [$atom_4 E] ] …
[rotate E [qx|qa E] [qy|qb E] [qz|qc E] ]…
[operate_on_points $sites]
[in_cartesian] [in_FC]
[translate [tx|ta E] [ty|tb E] [tz|tc E] ]…
[operate_on_points $sites]
[rand_xyz #displacement]
[in_cartesian] [in_FC]
[start_values_from_site $unique_site_name]
rigid defines a rigid body and associated translation and rotation operations. These operations are capable of creating and manipulating rigid bodies with hinges (torsion angles).
point_for_site defines a point in space with Cartesian coordinates given by the parameters ux, uy uz. Fractional equivalents can be defined using ua, ub and uc. $site is the site that the point_for_site represents.
z_matrix defines a point in space with coordinates given in Z-matrix format as follows::
- E can be an equation, constant or a parameter name with a value.
- $atom_1 specifies the site that the new Z-matrix point represents.
- The E after $atom_2 specifies the distance in Å between $atom_2 and $atom_1. $atom_2 must exist if $atom_1 is preceded by at least one point.
- The E $atom_3 specifies the angle in degrees between $atom_3-$atom_2- $atom_1. $atom_3 must exist if $atom_1 is preceded by at least two points.
- The E $atom_4 specifies the dihedral angle in degrees between the plane formed by $atom_3-$atom_2-$atom_1 and the plane formed by $atom_4-$atom_3-$atom_2. This angle is drawn using the right hand rule with the thumb pointing in the direction $atom_3 to $atom_2. $atom_4 must exist if $atom_1 is preceded by at least three sites of the rigid body.
- If $atom_1 is the first point of the rigid body then it is placed at Cartesian (0, 0, 0). If $atom_1 is the second point of the rigid body then it is placed on the positive z-axis at Cartesian (0, 0, E) where E corresponds to the E in [$atom_2 E]. If $atom_1 is the third point of the rigid body then it is placed in the x-y plane.
rotate rotates point_for_site’s an amount as defined by the rotate E equation around the vector defined by the Cartesian vector qx, qy, qz. The vector can be defined in fractional coordinates using qa, qb and qc instead.
translate performs a translation of point_for_site’s an amount in Cartesian equal to tx, ty, tz. The amount can be defined in fractional coordinates using ta, tb and tc instead.
If in_cartesian or in_FC is defined then the coordinates are interpreted as Cartesian or fractional atomic coordinates, respectively.
rotate and translate operates on any previously defined point_for_site’s; alternatively, point_for_site’s operated on can be identified using the operate_on_points keyword. The operate_on_points keyword must refer to previously defined point_for_site’s (see section 7.6 for a description of how to identify sites).
When continue_after_convergence is defined, rand_xyz processes are initiated after convergence. It introduces a random displacement to the translate fractional coordinates (tx, ty, tz) that are independent parameters. The size of the random displacement is given by the current temperature multiplied by #displacement where #displacement is in Å.
start_values_from_site initializes the values ta, tb, tc with corresponding values taken from the site $unique_site_name.
See section 7.10 for a description of rigid bodies.
[Rp #] [Rs #]
Defines the primary and secondary radius of the diffractometer in mm. The default is 217.5 mm.
[r_p #] [r_p_dash #] [r_wp #] [r_wp_dash #] [r_exp #] [r_exp_dash #] [gof #]
[weighted_Durbin_Watson #]
xdd dependent or global refinement indicators. Keywords ending in “_dash” correspond to background subtracted values, see section 5.6.
[scale E]
The Rietveld scale factor, can be applied to all phase types .
[scale_pks E]…
Used for applying intensity corrections to phase peaks. The following example defines a Lorentz-Polarisation correction:
scale_pks = (1+Cos(c Deg)^2 Cos(2 Th)^2)/(Sin(Th)^2 Cos(Th));
scale_pks is used for example in the LP_Factor, Preferred_Orientation and Absorption_With_Sample_Thickness_mm_Intensity macros.
[seed]
Initialises the random number generator with a seed based on the computer clock.
[site $site [x E] [y E] [z E] ]…
[occ $atom E [beq E]]…
[num_posns #] [rand_xyz !E] [inter !E #]
Defines a site where $site is a User defined string used to identify the site.
x, y, and z defines the fractional atomic coordinates, see also section 7.7.
occ and beq defines the site occupancy factor and the equivalent isotropic temperature factor beq. $atom corresponds to a valid atom symbol or isotope the data of which is contained in the file ATMSCAT.CPP for x-ray data and NEUTSCAT.CPP for neutron_data.
num_posns corresponds to the number of unique equivalent position generated from the space group; num_posns is updated on termination of refinement.
inter corresponds to the sum of all GRS interactions which are a function of the site. The value of inter can represent the site electrostatic potential depending on the type of GRS interactions defined.
Definition of a site fully occupied by aluminium:
site Al1 x 0 y 0 z 0.3521 occ Al+3 1 beq 0.3
Definition of a site occupied by two cations:
site Fe2 x 0.9283 y 0.25 z 0.9533 occ Fe+3 0.5 beq 0.25
occ Al+3 0.5 beq 0.25
[sites_distance N] | [sites_angle N] | [sites_flatten N [sites_flatten_tol !E]]…
[site_to_restrain $site [ #ep [ #n1 #n2 #n3 ] ] ]…
When used in equations the name N of sites_distance and sites_angle returns the distance in Å between two sites and angle in degrees between three sites respectively. The sites are defined by site_to_restrain.In particular N can be used in penalty equations to restrain bond lengths.
N of sites_flatten returns a restraint term that decreases as the sites become coplanar; it is defined as follows:
where tol corresponds to sites_flatten_tol, n corresponds to the number of sites defined with the site_to_restrain keyword, b are Cartesian unit length vectors between the sites and the geometric centre of the sites.
#eq, #n1, #n2 and #n3 correspond to the site equivalent position and fractional offsets to add to the sites. This is useful if the structure is already known and constraints are required, for example, in the bond length output (see append_bond_lengths):
Zr1:0 O1:20 0 0 -1 2.08772
O1:7 0 -1 0 2.08772 89.658
O1:10 0 0 -1 2.08772 90.342 90.342
O1:15 -1 0 0 2.08772 180.000 89.658 89.658
O1:18 -1 0 0 2.08772 90.342 89.658 180.000 90.342
P1:0 O1:4 0 0 0 1.52473
O1:8 0 0 0 1.52473 112.923
O1:0 0 0 0 1.52473 112.923 112.923
O2:0 0 0 0 1.59001 105.749 105.749 105.749
Example constraints using macros could look like the following:
Angle_Restrain(O1 P1 O1 8, 112, 112.92311, 0, 0.001)
Angle_Restrain(O1 18 -1 0 0 Zr1 O1 10 0 0 -1, 89, 89.65750, 0, 0.001)
Distance_Restrain(Zr1 O1 20 0 0 -1, 2.08, 2.08772, 0, 1)
BENZENE.INP demonstrates the use of the restraint macros Distance_Restrain, Angle_Restrain and Flatten. OpenGL viewing is recommended. Note, for more than 6 sites then sites_flatten becomes computationally expensive.
[sites_geometry $Name]…
[site_to_restrain $site [ #ep [ #n1 #n2 #n3 ] ] ]…
sites_geometry defines a grouping of up to four sites; $Name is the name given to ths grouping. The sites that are part of the group is defined using site_to_restrain, for example:
sites_geometry some_name
load site_to_restrain { C1 C2 C3 C4 }
Three functions, Sites_Geometry_Distance($Name), Sites_Geometry_Angle($Name) and Sites_Geometry_Dihedral_Angle($Name) can be used in equations to obtain the distance between sites C1 and C2, the angle between C1-C2-C3 and the dihedral angle formed between the planes C1-C2-C3 and C2-C3-C4. The convention used are the same as for z-matrices, see example SITES_GEOMETRY_1.INP:
If $Name contains only two sites then only Sites_Geometry_Distance($Name) can be used. Three sites defined additionally allows the use of Sites_Geometry_Angle($Name) and four sites defined additionally allows the use of Sites_Geometry_Dihedral_Angle($Name).
Examples SITES_GEOMETRY_1.INP and SITES_GEOMETRY_2.INP demonstartes the use of sites_geometry.
[siv_s1_s2 # #]
Defines the S1 and S2 integration limits for the spherical interaction volume of the GRS series.
[smooth #num_pts_left_right]
Performs a Savitzky-Golay smoothing on the observed data. The smoothing encompasses (2 * #num_pts_left_right + 1) points.
[spherical_harmonics_hkl $name]…
[sh_Cij_prm $Yij E]…
[sh_alpha !E]
[sh_order #]
Defines a hkl dependent symmetrized spherical harmonics series (see section 7.9.2). $name defines the name given to the series and when used in equations it returns the value of the spherical harmonics series.
sh_Cij_prm is the spherical harmonics coefficients, which can be defined by the User, or, alternatively if there are no coefficients defined then the sh_Cij_prm parameters are generated. Only the coefficients allowed by the selection rules of the point group are generated (Järvinen, 1993). At the end of refinement the generated sh_Cij_prm parameters are appended to sh_order. This allows for control over the sh_Cij_prm parameters in subsequent refinements. $Yij corresponds to valid symmetrized harmonics that has survived symmetrization. It is internally generated when there are no sh_Cij_prm parameters defined by the User.
sh_alpha corresponds to the angle in degrees between the polar axis and the scattering vector; sh_alpha defaults to zero degrees which is required for symmetric reflection as is the case for Bragg-Brentano geometry.
sh_order corresponds to the order of the spherical harmonic series which are even numbers ranging from 2 to 8 for non-cubic and from 2 to 10 for cubic systems.
The PO_Spherical_Harmonics macro simplifies the use of spherical_harmonics_hkl. CLAY.INP demonstrates the use of spherical_harmonics_hkl for describing anisotropic peak shapes.
[stacked_hats_conv [whole_hat E [hat_height E]]…[half_hat E [hat_height E]…]…
Defines hat sizes for generating an aberration function comprising a summation of hat functions. whole_hat defines a hat with an X axis extent of ±whole_hat/2. half_hat defines a hat with an X-axis range of half_hat to zero if half_hat<0; or zero to half_hat if half_hat> 0. hat_height defines the height of the hat; it defaults to 1. stacked_hats is used for example to describe tube tails using the Tube_Tails macro.
[start_X !E] [finish_X !E]
Defines the start and finish X region to fit to.
[str]…
Defines a new structure node.
[str_hkl_angle N h k l]…
Defines a parameter name and a vector normal to the plane defined by h, k and l. When the parameter name is used in an equation, it returns angles (in radians) between itself and the normal to the planes defined by hkls; see the Preferred_Orientation and PO_Two_Directions macros. An example in two directions is as follows:
[swap_sites $sites_1 $sites_2]…
swap_sites attempts to find a lower ![]() by swapping sites defined in $sites_1 with those defined in $sites_2. The swapping continues until all swaps are performed. Outline of the algorithm:
by swapping sites defined in $sites_1 with those defined in $sites_2. The swapping continues until all swaps are performed. Outline of the algorithm:
While swap_site processes still to be processed {
k = 0
Do
Randomize the cation configuration according to swap_sites.
k = k + 1
If ![]() (k+1) >
(k+1) > ![]() (k) then reset site positions
(k) then reset site positions
While ![]() (k+1) >
(k+1) > ![]() (k) or all swap possibility exhausted
(k) or all swap possibility exhausted
}
Starting from a particular cation configuration, a single swap of two different cation species does not exhaust all possible cation configurations. For example, three sites A, B and C have the six possible configurations of ABC, ACB, BAC, CAB, BCA, CBA. Swapping any two from the starting configuration of ABC results in the possible configurations of BAC, CBA, ACB with CAB and BCA absent. The absent configurations can be obtained by a double swap where, for example, the swapping of A and C yields CBA and then the swapping of A and B yields CAB. Thus all possible configurations can be visited if in between swapping steps are realized by the simulated annealing process.
Swapping the Zr sites with and Ca sites in the example above can be performed as follows:
swap_sites Ca Zr
If the sites were named Ca1, Ca2, Ca3, Zr1, Zr2, Zr3 then the following could be used:
swap_sites Ca* Zr*
[temperature !E]…
[move_to_the_next_temperature_regardless_of_the_change_in_rwp]
[save_values_as_best_after_randomization]
[use_best_values]
[do_processes]
A temperature regime has no affect unless the reserved parameter name T is used in val_on_continue attributes, or, if the following temperature dependent keywords are used:
randomize_on_errorsautomatically determines parameter displacements without the need for rand_xyzor val_on_continue. It performs well on a wide range of problems.
The reserved parameter T returns the current temperature and it can be used in equations and in particular the val_on_continue attribute. The first temperature defined becomes the starting temperature; subsequent temperature(s) become the current temperature.
If ![]() increases relative to a previous cycle then the temperature is advanced to the next temperature. If
increases relative to a previous cycle then the temperature is advanced to the next temperature. If ![]() decreases relative to previous temperatures of lesser values then the current temperature is rewound to a previous temperature such that its previous is of a greater value.
decreases relative to previous temperatures of lesser values then the current temperature is rewound to a previous temperature such that its previous is of a greater value.
move_to_the_next_temperature_regardless_of_the_change_in_rwp forces the refinement to move to the next temperature regardless of the change in Rwp from the previous temperature.
save_values_as_best_after_randomization saves the current set of parameters and gives them the status of “best solution”. Note, this does not change the global “best solution” which is saved at the end of refinement.
use_best_values replaces the current set of parameters with those marked as “best solution”.
do_processes executes any swap_sites or try_site_patterns processes.
The temperature regime as defined in the macro Auto_T is sufficient for most problems.
A typical temperature regime starts with a high value and then a series of annealing temperatures, for example:
temperature 2
move_to_the_next_temperature_regardless_of_the_change_in_rwp
temperature 1
temperature 1
temperature 1
If the current temperature is the last one defined (the fourth one), and ![]() decreased relative to the second and third temperatures, then the current temperature is set to the second temperature.
decreased relative to the second and third temperatures, then the current temperature is set to the second temperature.
The current temperature can be used in all equations using the reserved parameter T, for example:
x @ 0.123 val_on_continue = Val + T Rand(-.1, .1)
The following temperature regime will allow parameters to randomly walk for the first temperature. At the second temperature the parameters are reset to those that gave the “best solution”.
temperature 1
temperature 1 use_best_values
temperature 1
temperature 1 use_best_values
temperature 1
temperature 10
save_values_as_best_after_randomization
move_to_the_next_temperature_regardless_of_the_change_in_rwp
Note, that when a “best solution” is encountered the temperature is rewound to a position where the temperature decreased. For example, if the RWP dropped at lines 2 to 5 then the next temperature will be set to “line 1”.
The following will continuously use the “best solution” before randomisation. This particular temperature regime has a tendency to remain in a false minimum.
temperature 1 use_best_values
[th2_offset E]…
Used for applying 2q corrections to phase peaks. The following example applies a sample displacement correction:
th2_offset = -2 Rad © Cos(Th) / Rs;
th2_offset is used for example in the Zero_Error and Specimen_Displacement macros.
[try_site_patterns $sites [num_patterns_at_a_time #] ]…
try_site_patterns performs an exhaustive search of all possible cation configurations where the cations in question is identified by $sites. num_patterns_at_a_time defines the number of patterns to process at any one time. Outline of the algorithm:
While try_site_patterns processes still to be processed {
k = 0
Do
Change the cation configuration according to try_site_patterns
If ![]() (k+1) >
(k+1) > ![]() (k) then reset site positions
(k) then reset site positions
k = k + 1
While ![]() (k+1) >
(k+1) > ![]() (k) or k < num_patterns_at_a_time
(k) or k < num_patterns_at_a_time
}
The number of possible cation configurations determines the approximate magnitude of a structure determination problem. A structure consisting of NA cation sites of species A and NB cation sites of species B has, for a particular set of cation positions, a number of possible configurations NAB calculated as follows:
NAB = (NA+NB)CNB / NB!
where the notation uCv=(u-0)(u-1)(u-2)…(u-(v-1)) has been used. Thus for NA=3 and NB=4 we have NAB=(7 6 5 4)/(4 3 2 1)=NBA=(7 6 5)/(3 2 1)=35. The number of configurations NABD for and additional set of cation sites of species D becomes:
NABD = NAB ((NA+NB+NDD)CND / ND! )
An additional two D sites, or, NA=3, NB=4 and ND=2 gives and NABD=1260. Thus the number of configurations quickly becomes prohibitive for an exhaustive search.
Here is an example of using try_site_patterns on three Ca sites and two Zr sites:
str…
site Ca…
site Ca…
site Ca…
site Zr…
site Zr…
try_site_patterns “Ca Zr” num_patterns_at_a_time 3
NCaZr=10 and thus try_site_patterns will cycle through the 10 patterns searching for a reduction in ![]() .
.
[user_defined_convolution E min E max E]…
User defined convolutions are convoluted into phase peaks and can be a function of X. The min/max equations are mandatory, they define the x-axis extents of the user_defined_convolution where min ⇐ 0 and max >= 0. For example, a sinc function can be convoluted into phase peaks (example AU111.INP) as follows:
str
prm k 10 min 0.001 max 100
user_defined_convolution =
If(Abs(X) < 10^(-10), 1, (Sin(k X) /(k X))^2);
min -3 max 3
[use_tube_dispersion_coefficients]
Forces the use of Laboratory tube anomalous dispersion coefficients instead of the more accurate data from http://www‑cxro.lbl.gov/optical_constants/asf.html.
[verbose #]…
A value of 1 (the default) instructs the kernel to output in a verbose manner.
A value of 0 reduces kernel output such that text output is only initiated at the end of a refinement cycle.
A value of -1 reduces kernel output such that text output is initiated every second and only Rwp values at the end of a refinement cycle is kept.
The Simulated_Annealing_1 macro has verbose set to -1; this ensures that long simulated annealing runs do not exhaust memory due to saving Rwp values and text output buffers.
[view_structure]
Informs a driver GUI to display the structure.
[weighting !E [recal_weighting_on_iter]]
Used for calculating the xdd dependent weighting function in![]() , see equation Eq. (5‑2). Can be a function of the reserved parameter names X, Yobs, Ycalc and SigmaYobs. The default is as follows:
, see equation Eq. (5‑2). Can be a function of the reserved parameter names X, Yobs, Ycalc and SigmaYobs. The default is as follows:
weighting = 1 / Max(Yobs, 1);
In cases where weighting is a function of Ycalc then recal_weighting_on_iter can be used to recalculate the weighting at the start of refinement iterations. Otherwise the weighting is recalculated at the start of each refinement cycle.
Note that some goodness of fit indicators such as r_wp are a function of weighting, see Table 5‑2.
[weight_percent_amorphous !E]
Determines the amorphous content in a sample. The phase dependent keyword of spiked_phase_measured_weight_percent needs to be defined in order for weight_percent_amorphous to be calculated.
[x_calculation_step !E]
Calculation step used in the generation of phase peaks and fit_obj’s. Peak_Calculation_Step is the actual step size used, it is defined is as follows:
For and x-axis with equal steps and x_calculation_step not defined then
Peak_Calculation_Step = “Observed data step size” / convolution_step
otherwise
Peak_Calculation_Step = x_calculation_step / convolution_step
x_calculation_step can be a function of Xo and Th. In some situations it may be computationally efficient to write x_calculation_step in terms of the function Yobs_dx_at and the reserved parameter Xo. It is also mandatory to define x_calculation_step for data with unequal x-axis steps (*.xy or *.xye data files). Example uses of x_calculation_step is as follows:
x_calculation_step .01
x_calculation_step = .02 (1 + Tan(Th));
x_calculation_step = Yobs_dx_at(Xo);
[xdd $file [{ $data }] [range #] [xye_format] [gsas_format] [fullprof_format] ]…
Defines the start of xdd dependent keywords and the file containing the observed data.
{$data} allow for insertion of ASCII data directly into the INP file.
range applies to Bruker AXS *.RAW data files; in multi-range files it defines the range to be refined with the first range starting at 1. range is set to 1 by default.
xye_format (see section 10 as well) signals the loading of columns of x, y and error values; additional columns are ignored. gsas_format and fullprof_format signals the loading of GSAS and FullProf file formats.
The following instruction will refine on the first range in the data file pbso4.raw:
xdd pbso4.raw
To following will refine on the third range:
xdd pbso4.raw range 3
To read data directly from an INP file, the following can be used:
xdd {
1 1 10 ' start, step and finish (equidistant data)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
}
xdd {
_xy ' switch indicating x-y format
0.1 1 0.2 2 …
}
[xdd_out $file [append] ]…
Used for writing xdd dependent details to file. The out_eqn can contain the reserved parameter names of X, Yobs, Ycalc and SigmaYobs. See the keyword out for a description of out_record. The Out_Yobs_Ycalc_and_Difference macro is a good example of using xdd_out.
[xdd_scr $file] …
[dont_merge_equivalent_reflections]
[dont_merge_Friedel_pairs]
[ignore_differences_in_Friedel_pairs]
[str]…
[auto_scale !E]
[i_on_error_ratio_tolerance #]
[num_highest_I_values_to_keep #num]
xdd_scrdefines single crystal data from the file $file. The file can have extensions of *.HKL for ShelX HKL4 format or *.SCR for SCR format. All xdd and str keywords that are not dependent on powder data can be used by xdd_scr and hkl_Is_from_hkl4. Single crystal data is internally stored in 2q versus Fo2 format. This means that a lam definition is necessary and the keywords start_X, finish_X and exclude can be used with xdd_scr.
dont_merge_equivalent_reflections unmerges equivalent reflections, see also section 7.3.3.
dont_merge_Friedel_pairs prevents the merging of Friedel pairs.
ignore_differences_in_Friedel_pairs forces the use of Eq. (7‑12) for calculating F2.
auto_scale rewrites the scale parameter in terms of F2. This eliminates the need for the scale parameter. The value determined for auto_scale is updated at the end of refinement.
i_on_error_ratio_tolerance filters out hkl’s that does not meet the condition:
|Fo| > i_on_error_ratio_tolerance |Sigma(Fo)|
num_highest_I_values_to_keep removes all hkl’s except for #num hkl’s with the highest Fo values.
An example input segment for single crystal data refinement is as follows:
xdd_scr ylidm.hkl
MoKa2(0.001)
finish_X 35
weighting = 1 / (Sin(X Deg / 2) Max(1, Yobs));
STR(P212121)
a 5.9636
b 9.0390
c 18.3955
scale @ 1.6039731906
i_on_error_ratio_tolerance 4
site S1 x @ 0.8090 y @ 0.1805 z @ 0.7402 occ S 1 beq 2
site O1 x @ 0.0901 y @ 0.8151 z @ 0.2234 occ O 1 beq 2
…
The SCR format is white space delimited and consists of entries of h, k, l, m, d, 2q, Fo2 which is the format outputted by the Create_hklm_d_Th2_Ip_file macro.
[xo_Is]…
[xo E I E]…
Defines a phase type that uses x-axis space for generating peak positions, see example XOIS.INP. xo corresponds to the peak position and I is the intensity parameter before applying any scale_pks equations.
[yobs_eqn !N E]
The keyword yobs_eqn is used in place of the xdd keyword. It describes the observed data as an equation. This is very useful for approximating functions, see examples in section Error! Reference source not found.. The name given to the equation !N is used for identifying the equation in the GUI.
[yobs_out $file] [ycalc_out $file] [diff_out $file]
Outputs the observed, calculated and difference patterns respectively in a format as specified in the extension of $file. Extensions *.xy, *.scr, *.xdd are supported. Further formats are accommodated using any number of macros including Out_Yobs_Ycalc_and_Difference, Out_X_Yobs etc…
[yobs_to_xo_posn_yobs !E]
At the start of refinement yobs_to_xo_posn_yobs decomposes an X-ray diffraction pattern into a new pattern comprising at most one data point per hkl. Fitting to the decomposed pattern in a normal Rietveld refinement manner is then possible due to the ability to refine data of unequal x-axis step sizes. This normal Rietveld manner of fitting is important in structure solution from simulated annealing as the back ground can still be refined and the problem of peak overlap avoided. These new data points are not extracted intensities and thus the problem of peak overlap, as occurs in intensity extraction, is avoided. The much smaller number of data points in the new diffraction pattern can greatly improve speed in structure solution; in other words the calculation time in synthesizing the diffraction pattern becomes close to that of when dealing with single crystal data.
If the distance between two hkls is less than the value of yobs_to_xo_posn_yobs then the proposed data point at one of these hkls is discarded. Thus the final decomposed pattern may in fact have less data points than hkls. A reasonable value for yobs_to_xo_posn_yobs is Peak_Calculation_Step, or,
yobs_to_xo_posn_yobs = Peak_Calculation_Step;
yobs_to_xo_posn_yobs can be a function of the reserved parameter X with X being the value of the x-axis at the hkl.
It is important to determine and then fix all peak shape, zero error and lattice parameters before using yobs_to_xo_posn_yobs. Also, if the original diffraction pattern is noisy then it may be best to smooth it using the smooth keyword or re-binned using rebin_with_dx_of. Alternatively, a calculated pattern could be used as input into the yobs_to_xo_posn_yobs
Note that structure solution can be speed up by preventing graphical output or by increasing the Graphics Response Time in the GUI.
See examples CIME-DECOMPOSE.INP and PBSO4-DECOMPOSE.INP.
8.3 Keywords to simplify User input
8.3.1 The "load { }" keyword and attribute equations
The ”load { }“ keyword can be used to simplify User input. It allows the loading of keywords of the same type by typing the keywords once, for example, the exclude keyword in the following input segment:
xdd…
exclude 20 22
exclude 32 35
exclude 45 47
can be rewritten using ”load { }“ as follows:
xdd…
load exclude { 20 22 32 35 45 47 }
This input can be further simplified using the Exclude macro:
Exclude { 20 22 32 35 45 47 }
In some cases attribute equations are loaded by the parameter itself. For example, in the following:
prm t 0.01 val_on_continue = Rand(-Pi, Pi); min 0.4 max 0.5
the prm will actually load the attribute. But, in the following:
load prm val_on_continue min max { t 0.01 = Rand(-Pi, Pi); 0.4 0.5 }
the load keyword will load the attributes.
The following is valid:
load sh_Cij_prm
{
y00 !sh_c00 1
y20 sh_c20 0.26202642 min 0 max 1
y40 sh_c40 0.06823548
…
}
In this case the load keyword does not contain min/max and the parameter will load its attributes. The load keyword however can contain attributes, for example:
load sh_Cij_prm min max
{
y00 !sh_c00 1 0 1
y20 sh_c20 0.26202642 0 1
y40 sh_c40 0.06823548 0 1
…
}
In this case the attributes must be entered for all load entries.
8.3.2 The "move_to $keyword" keyword
The move_to keyword provides a means of entering parameter attributes without having to first load the parameter name and value, see for example the Keep_Atom_Within_Box macro. The site dependent ADPs_Keep_PD macro defines min/max limits; here's part of that macro:
move_to u12
min = -Sqrt(Get(u11) Get(u22));
max = Sqrt(Get(u11) Get(u22));
The $keyword of move_to can be any keyword and not just a parameter keyword.
8.3.3 The "for xdds { }" and "for strs { }" constructs
The “for xdds { }” and ”for strs { }“ constructs simplify the construction of input files when there are multiple diffraction patterns with similar structures, see example QUARTZ2_FPA.INP. For example, two diffraction patterns with the same structures can be composed as follows:
| xdd … | ‘ first xdd |
| bkg … th2_offset … … | ‘ xdd dependent, not common to the xdd's |
| str… | ‘ first str |
| scale … … | ‘ str dependent, not common to the str's |
| xdd … | ‘ second xdd |
| bkg … th2_offset … … | ‘ xdd dependent, not common to the xdd's |
| str… | ‘ second str |
| scale … … | ‘ str dependent, not common to the str's |
| for xdds { | |
| Slit_Width(.2) CuKa2 … | ‘ xdd dependent, common to the xdd's |
| for strs { | ‘ str dependent, common to the xdd's |
| … | |
| } | |
| for strs 1 to 1 { | |
| space_group p1 site … | ‘ str dependent, specific to the first str |
| } | |
| } |
For obvious reasons, parameters should not be given the @ name within for constructs. The effect this would have is to give unique parameter names to the parameters iterated over; the output file would contain the parameter value corresponding to the last “for xdds” or “for strs” iteration.
9 Macros and Include Files
INP files are pre-processed. The pre-processor comprises directives beginning with the character # and macros. Macros are used for grouping keywords. The directives are of two types, global directives and directives that are invoked on macro expansion, they are:
Directives with global scope
macro $user_defined_macro_name { … }
#include $user_defined_macro_file_name
#delete_macros { $macros_to_be_deleted }
#define, #undef, #ifdef, #ifndef, #else, #endif
Directives invoked on macro expansion
#m_ifarg, #m_else, #m_endif
#m_code, #m_eqn, #m_code_refine, #m_one_word
#m_argu, #m_first_word, #m_unique_not_refine
9.1 The macro directive
Macros are defined using the macro directive; here's an example:
macro Cubic(cv)
{
a cv
b = Get(a);
c = Get(a);
}
Macros can have multiple arguments or none at all; the Cubic macro above has one argument; here are some examples of the use of Cubic:
Cubic(4.50671)
Cubic(a_lp 4.50671 min 4.49671 max 4.52671)
Cubic(!a_lp 4.50671)
The first instance defines the a, b and c lattice parameters without a parameter name. The second defines the lattice parameters with a name indicating refinement of the a_lp parameter. In the third example, the a_lp parameter is preceded by the character !. This indicates that the a_lp parameter is not to be refined; it can however be used in equations. The definition of macros need not precede its use. For example, in the segment:
xdd…
Emission_Profile ' this is expanded
macro Emission_Profile { CuKa2(0.001) }
Emission_Profile is expanded to “CuKa2(0.001)” even though Emission_Profile has been defined after its use.
Macro names need not be unique; in cases where more than one macro have the same name then the actual macro expanded is determined by the number of arguments. For example, if the macro Slit_Width(.1) is used then the Slit_Width(v) macro is expanded. On the other hand if the macro Slit_Width(sw, .1) is used then the Slit_Width(c, v) macro is expanded.
Macros can also expand to other macro names. For example, the macro Crystallite_Size expands to CS and since CS is a macro then the CS macro will be expanded.
9.1.1 Directives with global scope
#include $user_defined_macro_file_name
Include files are used to group macros. The file TOPAS.INC contains standard macros; a good place to view examples. Text within include files are inserted at the position of the #include directive, thus the following:
#include “my include file.inc”
inserts the text within ”my include file.inc“ at the position of the #include directive. The standard macro file TOPAS.INC is always included by default.
#delete_macros { $macros_to_be_deleted }
Macros can be deleted using the #delete_macroskeyword, for example,
#delete_macros { LP_Factor SW ZE }
will delete all macros previously defined with the names LP_Factor, SW and ZE including macros of the same name but with different arguments.
#define, #undef, #ifdef, #ifndef, #else, #endif
The #define and #undef directives works similar to the c pre-processor directives of the same name. #define and #undef is typically used with #ifdef, #else, #endif directives to control macro expansion in INP files. For example, the following:
#ifdef STANDARD_MACROS
xdd…
#endif
will expand to contain the xdd keyword if STANDARD_MACROS has been previously defined using a #define directive. The following will also expand to contain the xdd keyword if STANDARD_MACROS has not been defined using a #define directive,
#ifdef !STANDARD_MACROS
#define STANDARD_MACROS
xdd…
#endif
or,
#ifndef STANDARD_MACROS
#define STANDARD_MACROS
xdd…
#endif
Note the use of the ‘!’ character placed before STANDARD_MACROS which means if STANDARD_MACROS is not defined.
9.1.2 Directives invoked on macro expansion
#m_ifarg, #m_else, #m_endif
These are conditional directives that are invoked on macro expansion. #m_ifarg operates on two statements immediately following its use; the first must refer to a macro argument and the second can be any of the following: #m_code, #m_eqn, #m_code_refine, #m_one_word and “some string”. #m_ifarg evaluates to true according to the rules of Table 9‑1.
Table 9‑1 #m_ifarg syntax and meaning.
| Evaluates to true if the following is true | |
| #m_ifarg c #m_code | If the macro argument c has a letter or the character ! as the first character and if it is not an equation. |
| #m_ifarg c #m_eqn | If the macro argument c is an equation. |
| #m_ifarg c #m_code_refine | If the macro argument c has a letter as the first character and if it is not an equation. |
| #m_ifarg c “some_string” | If the macro argument c == “some_string”. |
| #m_ifarg v #m_one_word. | If the macro argument v consists of one word. |
#m_argu, #m_first_word, #m_unique_not_refine
These operate on one macro argument with the intention of changing the value of the argument according to the rules of Table 9‑2.
Table 9‑2 Directives that operate and maybe change the value of a macro argument.
| Meaning | |
| #m_argu c | Change the macro argument c to a unique parameter name if it has @ as the first character. |
| #m_unique_not_refine c | Change the macro argument c to a unique parameter name that is not to be refined. |
| #m_first_word v | Replace the macro argument v with the first word in the macro argument v. |
9.2 Overview
The file TOPAS.INC is included into INP files by default; it contains commonly used standard macros. The meaning of the macro arguments in TOPAS.INC can be readily determined from the following conventions:
Ø Arguments called “c” correspond to a parameter name.
Ø Arguments called “v” correspond to a parameter value.
Ø Arguments called “cv” correspond to a parameter name and/or value.
For example, the macro Cubic(cv) requires a value and/or a parameter name as an argument. Some examples are:
Cubic(a_lp 10.604)
Cubic(10.604)
Cubic(@ 10.604 min 10.59 max 10.61)
Here are some more examples for the Slit_Width macro:
SW(@, .1)
SW(sw, .1 min = Val-.02; max = Val+.02;)
SW((ap+bp)/cp, 0) ' where ap, bp anc cp are parameters defined elsewhere
9.2.1 xdd macros
RAW(path_no_ext)
RAW(path_no_ext, range_num)
DAT(path_no_ext)
XDD(path_no_ext)
XY(path_no_ext, calc_step)
XYE(path_ext)
SCR(path_no_ext)
SHELX_HKL4(path_no_ext)
9.2.2 Lattice parameters
Cubic(cv)
Tetragonal(a_cv, c_cv)
Hexagonal(a_cv, c_cv)
Rhombohedral(a_cv, al_cv)
9.2.3 Emission profile macros
| No_Th_Dependence CuKa1(yminymax) CuK1sharp(yminymax) CuKa2_analyt(yminymax) CuKa2(yminymax) CuKa4_Holzer(yminymax) CuKa5(yminymax) CuKa5_Berger(yminymax) CoKa3(yminymax) CoKa7_Holzer(yminymax) CrKa7_Holzer(yminymax) | FeKa7_Holzer(yminymax) MnKa7_Holzer(yminymax) NiKa5_Holzer(yminymax) MoKa2(yminymax) CuKb4_Holzer(yminymax) CoKb6_Holzer(yminymax) CrKb5_Holzer(yminymax) FeKb4_Holzer(yminymax) MnKb5_Holzer(yminymax) NiKb4_Holzer(yminymax) |
9.2.4 Instrument and instrument convolutions
Radius(rp, rs)
Primary and secondary instrument radii in [mm]. For most diffractometers rp equals rs.
Specimen_Tilt(c, v)
Specimen tilt in mm.
Slit_Width(c, v) or SW(c, v)
Aperture of the receiving slit in the equitorial plane in mm.
Sample_Thickness(dc, dv)
Sample thickness in mm in the direction of the scattering vector.
Divergence(c, v)
Horizontal divergence of the beam in degrees in the equitorial plane.
Variable_Divergence(c, v)
Variable_Divergence_Shape(c, v)
Variable_Divergence_Intensity
Constant illuminated sample length in mm for variable slits (i.e. variable beam divergence). This Variable_Divergence macro applies both a shape and intensity correction.
Simple_Axial_Model(c, v)
Receiving slit length mm for describing peak asymmetry due to axial divergence.
Full_Axial_Model(filament_cv, sample_cv, detector_cv, psol_cv, ssol_cv)
Accurate model for describing peak asymmetry due to axial divergence of the beam.
[filament_cv]: Tube filament length in [mm].
[sample_cv]: Sample length in axial direction in [mm].
[detector_cv]: Length of the detector (= receiving) slit in [mm].
[psol_cv, ssol_cv]: Aperture of the primary and secondary Soller slit in [°].
Finger_et_al(s2, h2)
Finger et al., 1994. model for describing peak asymmetry due to axial divergence.
[s2, h2]: Sample length, receiving slit length.
Tube_Tails(source_width_c, source_width_v, z1_c, z1_v, z2_c, z2_v, z1_z2_h_c, z1_z2_h_v)
Model for description of tube tails (Bergmann, 2000).
[source_width_c, source_width_v]: Tube filament width in [mm].
[z1_c, z1_v]: Effective width of tube tails in the equatorial plane perpendicular to the X-ray beam - negative z-direction [mm].
[z2_c, z2_v]: Effective width of tube tails in the equatorial plane perpendicular to the X-ray beam - positive z-direction [mm].
[z1_z2_h_c, z1_z2_h_v]: Fractional height of the tube tails relative to the main beam.
UVW(u, uv, v, vv, w, wv)
Cagliotti relation (Cagliotti et al., 1958).
[u, v, w]: Parameter names.
[uv, vv, wv]: Halfwidth value.
9.2.5 Phase peak_type's
PV_Peak_Type(ha, hav, hb, hbv, hc, hcv, lora, lorav, lorb, lorbv, lorc, lorcv)
TCHZ_Peak_Type(u, uv, v, vv, w, wv, x, xv, y, yv, z, zv)
PVII_Peak_Type(ha, hav, hb, hbv, hc, hcv, ma, mav, mb, mbv, mc, mcv)
Pseudo-Voigt, TCHZ pseudo-Voigt and PearsonVII functions.
For the definition of the functions and function parameters refer to section 0.
9.2.6 Quantitative Analysis
Apply_Brindley_Spherical_R_PD( R, PD)
Applies the Brindley correction for quantitative analysis (Brindley, 1945).
MVW(m_v, v_v, w_v)
Returns cell mass, cell volume and weight percent.
9.2.7 2q Corrections
Zero_Error or ZE(c, v)
Zero point error.
Specimen_Displacement(c, v) or SD(c, v)
Specimen displacement error.
9.2.8 Intensity Corrections
LP_Factor(c, v)
Lorentz and Lorentz-Polarisation factor.
[c, v]: Monochromator angle in [°2q]
For unpolarized radiation v is 90 (e.g. X-ray diffractometers without any monochromator), for fully polarized radiation v is 0 (e.g. synchrotron radiation).
Values for most common monochromators (Cu radiation) are:
Ge : 27.3
Graphite : 26.4
Quartz : 26.6
Lorentz_Factor
Lorentz_Factor for fixed wavelength neutron data.
Surface_Roughness_Pitschke_et_al(a1c, a1v, a2c, a2v)
Surface_Roughness_Suortti(a1c, a1v, a2c, a2v)
Suortti and Pitschke_et_al intensity corrections each with two parameters a1 and a2.
Preferred_Orientation(c, v, ang, hkl) or PO(c, v, ang, hkl)
Preferred orientation correction based on March (1932).
[c, v]: March parameter value.
[ang, hkl]: Lattice direction.
PO_Two_Directions(c1, v1, ang1, hkl1, c2, v2, ang2, hkl2, w1c, w1v)
Preferred orientation correction based on March (1932) considering two preferred orientation directions.
[c1, v1]: March parameter value for the first preferred orientation direction.
[ang1, hkl1]: Parameter name and lattice plane for the first preferred orientation direction.
[c2, v2]: March parameter value for the second preferred orientation direction.
[ang2, hkl2]: Lattice direction for the second preferred orientation direction.
[w1c, w1v]: Fraction of crystals oriented into first preferred orientation direction.
PO_Spherical_Harmonics(sh, order)
Preferred orientation correction based on spherical harmonics according to Järvinen (1993).
[(sh, order)]: Parameter name, spherical harmonics order.
9.2.9 Bondlength penalty functions
Anti_Bump(ton, s1, s2, ro, wby)
AI_Anti_Bump(s1, s2, ro, wby, num_cycle_iters), AI_Anti_Bump(s1, s2, ro, wby)
Applies a penalty function as a function of the distance between atoms. The closer the atoms are the higher the penalty is.
[ton]: Sets to_N of the box_interaction keyword.
[s1, s2]: Sites.
[ro]: Distance.
[wby]: Relative weighting given to the penalty function.
For more details refer to box_interaction and ai_anti_bump..
Parabola_N(n1, n2, s1, s2, ro, wby)
Applies a penalty function as a function of the distance between atoms. The closer the atoms are the higher the penalty is.
[n1]: The closest n1 number of atoms of type s2 is soft constrained to a distance ro away from s1 .
[n2]: The closest n2 number of atoms of type s2 (excluding the closest n1 number of atoms of type s2) is repelled from s1, if the distance between s1 and s2 is less than ro .
[s1, s2]: Sites.
[ro]: Distance.
[wby]: Relative weighting given to the penalty function.
Grs_Interaction(s1, s2, wqi, wqj, c, ro, n)
Penalty function applying the GRS series according to Coelho & Cheary (1997).
[s1, s2]: Sites.
[wqi, wqj]: Valence charge of the atoms.
[c]: Name of the GRS.
[ro]: Distance.
[n]: The exponent of the repulsion part of the Lennard-Jones potential.
For more details refer to grs_interaction.
Grs_No_Repulsion(s1, s2, wqi, wqj, c)
Used for calculating the Madelung constants.
[s1, s2]: Sites.
[wqi, wqj]: Valence charge of the atoms.
[c]: Name of the GRS.
Grs_BornMayer(s1, s2, wqi, wqj, c, ro, b)
Uses the GRS series with a Born-Mayer equation for the repulsion term.
[s1, s2]: Sites.
[wqi, wqj]: Valence charge of the atoms.
[c]: Name of the GRS.
[ro]: Mean distance.
[b]: b-constant for the repulsion part of the Born-Mayer potential.
Distance_Restrain(sites, t, t_calc, tol, wscale)
Angle_Restrain(sites, t, t_calc, tol, wscale)
Flatten(sites, t_calc, tol, wscale)
Distance_Restrain_Keep_Within(sites, r, wby, num_cycle_iters)
Distance_Restrain_Keep_Out(sites, r, wby, num_cycle_iters)
Applies penalties restraining distances and angles between sites. .
'sites' must comprise two sites for the distance restraints and three for the angle restraints.. For Flatten 'sites' must contain more than three sites. wby is a scaling constant applied to the penalty.
Keep_Atom_Within_Box(size) - this is a constraint macro.
Applies constraints such that the present site cannot more outside of a box with a length of 2*size.
9.2.10 Reporting macros
Create_2Th_Ip_file(file)
Creates a file with positions (2) and intensities.
Create_d_Ip_file(file)
Creates a file with positions (d) and intensities.
Create_hklm_d_Th2_Ip_file(file)
Creates a file with the following information for each peak: h, k, l, multiplicity, positions d and 2q and intensities.
Out_Yobs_Ycalc_and_Difference(file)
Outputs the x-axis, Yobs, Ycalc and difference.
Out_X_Yobs(file), Out_X_Ycalc(file), Out_X_Difference(file)
Outputs the x-axis, Yobs, Ycalc and Difference.to files.
Out_F2_Details(file), Out_A01_A11_B01_B11(file)
Outputs structure factor details, see section 7.3.2.
Out_FCF(file)
Outputs a CIF file representation of structure factor details suitable for generating Fourier maps using ShelX..
Out_CIF_STR(file)
Outputs structure details in CIF format.
9.2.11 Rigid body macros
Set_Length(s0, s1, r, xc, yc, zc, cva, cvb)
Fixes the distance between two sites.
[s0, s1]: Site names.
[r]: Distance in Angstroms.
[xc, yc, zc]: The parameter names for the coordinates of s0.
[cva, cvb]: Parameter names and values for rotations about the x and y axes
Set_Lengths(s0, s1, s2, r, xc, yc, zc, cva1, cvb1, cva2, cvb2)
Set_Lengths(s0, s1, s2, s3, r, xcv, ycv, zcv, cva1, cvb1, cva2, cvb2, cva3, cvb3)
Fixes the distance between two and three sites, respectively.
Set_Lengths(s0, s1, s2, r, xc, yc, zc, cva1, cvb1, cva2, cvb2) is defined as
macro Set_Lengths(s0, s1, s2, r, xc, yc, zc,cva1, cvb1, cva2, cvb2)
{
Set_Length(s0, s1, r, xc, yc, zc, cva1, cvb1)
Set_Length(s0, s2, r, xc, yc, zc, cva2, cvb2)
}
and so on.
Triangle(s1, s2, s3, r)
Triangle(s0, s1, s2, s3, r)
Triangle(s0, s1, s2, s3, r, xc, yc, zc, cva, cvb, cvc)
Defines a regular triangle without and with a central atom (s0).
[s0, s1, s2, s3]: Site names. s0 is the central atom of the triangle.
[r]: Distance in Angstroms.
[xc, yc, zc]: Parameter names for the fractional coordinates of the geometric center of the triangle.
[cva, cvb, cvc]: Parameter names and values for rotations about the x, y and z axes.
Tetrahedra(s0, s1, s2, s3, s4, r, xc, yc, zc, cva, cvb, cvc)
Defines a tetrahedra with a central atom.
[s0, s1, s2, s3, s4]: Site names. s0 is the central atom of the tetrahedra.
[r]: Distance in Angstroms.
[xc, yc, zc]: Parameter names for the fractional coordinates of the geometric center of the tetrahedra.
[cva, cvb, cvc]: Parameter names and values for rotations about the x, y and z axes.
Octahedra(s0, s1, s2, s3, s4, s5, s6, r)
Octahedra(s0, s1, s2, s3, s4, s5, s6, r, xc, yc, zc, cva, cvb, cvc)
Defines an octahedra with a central atom.
[s0, s1, s2, s3, s4, s5, s6]: Site names. s0 is the central atom of the octahedra.
[r]: Distance in Angstroms.
[xc, yc, zc]: Parameter names for the fractional coordinates of the geometric center of the octahedra.
[cva, cvb, cvc]: Parameter names and values for rotations about the x, y and z axes.
Hexagon_sitting_on_point_in_xy_plane(s1, s2, s3, s4, s5, s6, a)
Hexagon_sitting_on_side_in_xy_plane(s1, s2, s3, s4, s5, s6, a)
Defines a regular hexagon, where the hexagon is sitting on a point or on a side in the x-y plane, respectively.
[s1, s2, s3, s4, s5, s6]: Site names.
[a]: Distance in Angstroms.
Translate(acv, bcv, ccv)
Translate(acv, bcv, ccv, ops)
Performs a translation of the rigid body.
[acv, bcv, ccv]: Amount of the translation in fractional coordinates.
[ops]: Operates on previously defined sites in “ops”.
Translate_with_site_start_values(s0, xc, yc, zc)
Performs a translation using the coordinates of s0 as start values.
[s0]: Site name.
[xc, yc, zc]: Parameter names for the coordinates of s0.
Rotate_about_points(cv, a, b)
Rotate_about_points(cv, a, b, pts)
Performs a rotation about a rotation vector specified by two sites.
[cv]: Amount the rigid body is rotated about the specified rotation vector in degrees.
[a, b]: Rotation vector defined by the sites a and b.
[pts]: Operates on previously defined point_for_site(s).
Note: Do not include points rotated about in the “operate on points” list of the
Rotate_about_points macro. For example, in
Rotate_about_points(@ 1 0, C1, C2, ” C3 C4 C5 C6 “)
the points C1 and C2 are not included in the “points operated on” list. Note also that Rotate_about_points without a “points operated on” list will operate on all previously defined point_for_site(s). Therefore, when an “operate on points” list is not defined then it is necessary to place the “points rotated about” after the Rotate_about_points macro. It is best to specify an “operate on points” list when in doubt.
Rotate_about_these_points(cv, a, b, ops)
Performs a rotation about a rotation vector specified by two sites.
[cv]: Amount the rigid body is rotated about the specified rotation vector in degrees.
[a, b]: Rotation vector defined by the sites a and b.
[ops]: Operates on previously defined point_for_site(s).
Rotate_about_axies(cva, cvb)
Rotate_about_axies(cva, cvb, cvc)
Performs a rotation about the axis of the rigid body.
[cva, cvb, cvc]: Parameter names and values for rotations about the x, y and z axes.
Rotation_vector_from_points(a, b)
Determines a rotation vector form two points.
[a, b]: Rotation vector defined by the sites a and b.
9.2.12 Background functions using fit_objects
One_on_X(c, v)
1/X background function ideal to describe background intensity at low angles due to air scattering
Bkg_Diffuse(b, bv, bb, bbv)
Defines a function to describe short range order effects.
[b, bv]: Parameter name, refineable weight.
[bb, bbv]: Parameter name, correlation shell radii.
PV(a, xo, fwhm, g)
PV(a, xo, fwhm, g, av, xov, fwhmv, gv)
Defines a pseudo-Voigt function.
[a, av]: Parameter name, area.
[xo, xov]: Parameter name, Position in [° 2q].
[fwhm, fwhmv]: Parameter name, full width at half maximum in [° 2q].
[g, gv]: Parameter name, pseudo-Voigt mixing parameter.
PV_Left_Right(a, xo, fwhm1, fwhm2, g)
PV_Left_Right(a, xo, fwhm1, fwhm2, g, av, xov, fwhm1v, fwhm2v, gv)
Defines a split-pseudo-Voigt function.
[a, av]: Parameter name, area.
[xo, xov]: Parameter name, Position in [° 2q].
[fwhm1, fwhm1v]: Full width at half maximum in [° 2q] for the left composite function.
[fwhm2, fwhm2v]: Full width at half maximum in [° 2q] for the right composite function.
[g, gv]: Pseudo-Voigt mixing parameter.
9.2.13 Sample convolutions
Absorption(c, v), AB(c, v)
Linear absorption coefficient in t in cm-1 used for adjusting the peak shape due to sample transparency.
Absorption_With_Sample_Thickness_mm_Shape(u, uv, d, dv)
Corrects the peak shape for absorption effects.
[u, uv]: Parameter name, linear absorption coefficient in cm-1.
[d, dv]: Parameter name, sample thickness in [mm].
Absorption_With_Sample_Thickness_mm_Shape_Intensity(u, uv, d, dv)
Corrects the peak intensity for absorption effects.
[u, uv]: Parameter name, absorption coefficient in cm-1.
[d, dv]: Parameter name, sample thickness in [mm].
CS_L(c,v) or Crystallite_Size(c, v) or CS(c, v)
Applies a Lorentzian convolution with a FWHM that varies according to the relation lor_fwhm = c / Cos(Th).
[c, v]: Parameter name, crystallite size in [nm].
CS_G(c, v)
Applies a Gaussian convolution with a FWHM that varies according to the relation gauss_fwhm = c / Cos(Th).
[c, v]: Parameter name, crystallite size in [nm].
Strain_L(c, v) or Microstrain(c, v) or MS(c, v)
Applies a Lorentzian convolution with a FWHM that varies according to the relation lor_fwhm = c Tan(Th).
Strain_G(c, v)
Applies a Gaussian convolution with a FWHM that varies according to the relation gauss_fwhm = c Tan(Th).
LVol_FWHM_CS_G_L(k, lvol, kf, lvolf, csgc, csgv, cslc, cslv)
Calculates FWHM and IB (integral breadth) based volume-weighted column heights (LVol). For details refer to section 7.2.
[k, lvol]: shape factor (fixed to 1), integral breadth based LVol.
[kf, lvolf]: shape factor (defaults to 0.89), FWHM based LVol.
[csgc, csgv]: Parameter name, Gaussian component.
[cslc, cslv]: Parameter name, Lorentzian component.
9.2.14 Neutron TOF
TOF_XYE(path, calc_step), TOF_GSAS(path, calc_step)
Includes the neutron_data keyword and the calculation step size.
TOF_LAM(w_ymin_on_ymax)
Defines a simple emission profile suitable for TOF data
TOF_x_axis_calibration(t0, t0v, t1, t1v, t2, t2v)
Writes the pk_xo equation in terms of the three calibration constants t0, t1, t2 converting d-spacing to x-axis space.
TOF_Exponential(a0, a0v, a1, a1v, wexp, t1, lr)
An exponential convolution applied to the TOF peaks - see example TOF_BANK2_1.INP.
TOF_CS_L(c, v, t1), TOF_CS_G(c, v, t1)
Lorentzian and Gaussian components for crystallite size. t1 is the calibration constant appearing in the argument of the macro TOF_x_axis_calibration.
TOF_PV(fwhm, fwhmv, lor, lorv, t1)
A pseudo-Voigt used to describe the instrumental broadening t1 is the calibration constant appearing in the argument of the macro TOF_x_axis_calibration, see examples tof_balzar_br1.inp and tof_balzar_sh1.inp.
9.2.15 Miscalleneous
Temperature_Regime
Defines a temperature regime. See the temperature keyword.
STR(sg)
Signals the start of structure information with a space group of sg.
Exclude
Defines excluded regions. See the exclude keyword.
Decompose(diff_toll)
Decompose a diffraction pattern into data points at peak positions only. Data points closer than diff_toll to another data point is not included. Decompose also sets x_calculation_step to the value of diff_toll.
ADPs_Keep_PD
Mixture_LAC_1_on_cm(mlac)
Phase_Density_g_on_cm3(pd)
Phase_LAC_1_on_cm(u)
Gauss(xo, fwhm), Lorentzian(xo, fwhm)
An equation defines a unit area Gaussian or Lorentzian with a position of xo and a FWHM of fwhm
10 File types and formats
| Table 10‑1 File types. | |
| File Type | Comments |
| *.PRO | Project files. |
| *.INP | INP format Input file. |
| *.OUT | Output file created on termination of refinement. Same format as *.INP. |
| *.STR | Structure data. Same format as *.INP. |
| *.LAM | Source emission profile data. Same format as *.INP. |
| *.DEF | Program defaults. Same format as *.INP. |
| *.LOG | TOPAS.log and Tc.log. Useful for tracking input errors. |
| Measurement Data | |
| *.RAW | Bruker AXS binaries (DIFFRAC AT and DIFFRACplus) |
| *.DAT *.XDD / *.CAL *.XY, *XYE | ASCII file formats, see Table 10‑2 |
| *.SCR | ASCII file format comprising lines of h, k, l, m, d, 2q, and Fo. |
| *.HKL | ShelX HKL4 format. |
| Structure and structure factor data | |
| *.CIF | Crystallographic Information File; International Union for Crystallography (IUCr). |
| *.FCF | CIF file representation of structure factor details suitable for generating Fourier maps using ShelX. |
| Table 10‑2 ASCII input data file formats. *.XY, *.XYE, *.XDD and *.CAL are delimited by white space characters and can contain line and block comments. | ||
| File Type | Format | Explanation |
| *.DAT, LHPM/RIET7/CSRIET | ||
| Line 1-4 | Comments | |
| Line 5 | Start angle, step width, finish angle | |
| Line 6 onwards | Observed XRD data points (any number of rows) | |
| GSAS (“std - const”, “alt - ralf”), use keyword gsas_format | ||
| Line 1 | Legend | |
| Line 2 | Item 3: Number of data points | |
| Line 3 onwards | Depending of item10 and item5 | |
| For item10 = “STD” and item5 = “CONST” xmin = item6/div step =item7/div read(10(i2,F6.0) iww(i),y(i) i=1, npts sigma(i)=sqr(y(i)/iww(i)) i=1, npts For item10 = “ALT” and item5 = “RALF” xmin = item6/32 step = item7/32 read(4(F8.0,F7.4,F5.4) x(i), y(i), sigma(i) i=1, npts x(i) = x(i)/32 i=1, npts do i = 1, npts-1 div = x(i+1)-x(i) y(i) =1000 * y(i)/div sigma(i) = 1000 * sigma(i)/div end do rk (constant wavelength data): div = 100 rk (time of flight data): div = 1 | ||
| FullProf (INSTRM = 0: free format file), use keyword fullprof_format | ||
| Line 1 | Start angle, step width, finish angle, comments | |
| Line 2 onwards | Observed XRD data points (any number of rows) | |
| *.XDD / *.CAL | Line 1 | Optional line for comments |
| Number 2 | Start angle | |
| Number 3 | Step width | |
| Number 4 | Finish angle | |
| Number 5 | Counting time | |
| Number 6 | Unused | |
| Number 7 | Unused | |
| Number 8 onwards | Observed XRD data points | |
| *.XY | 2q and intensity data values | |
| *.XYE | 2q, intensity and intensity error values. | |
